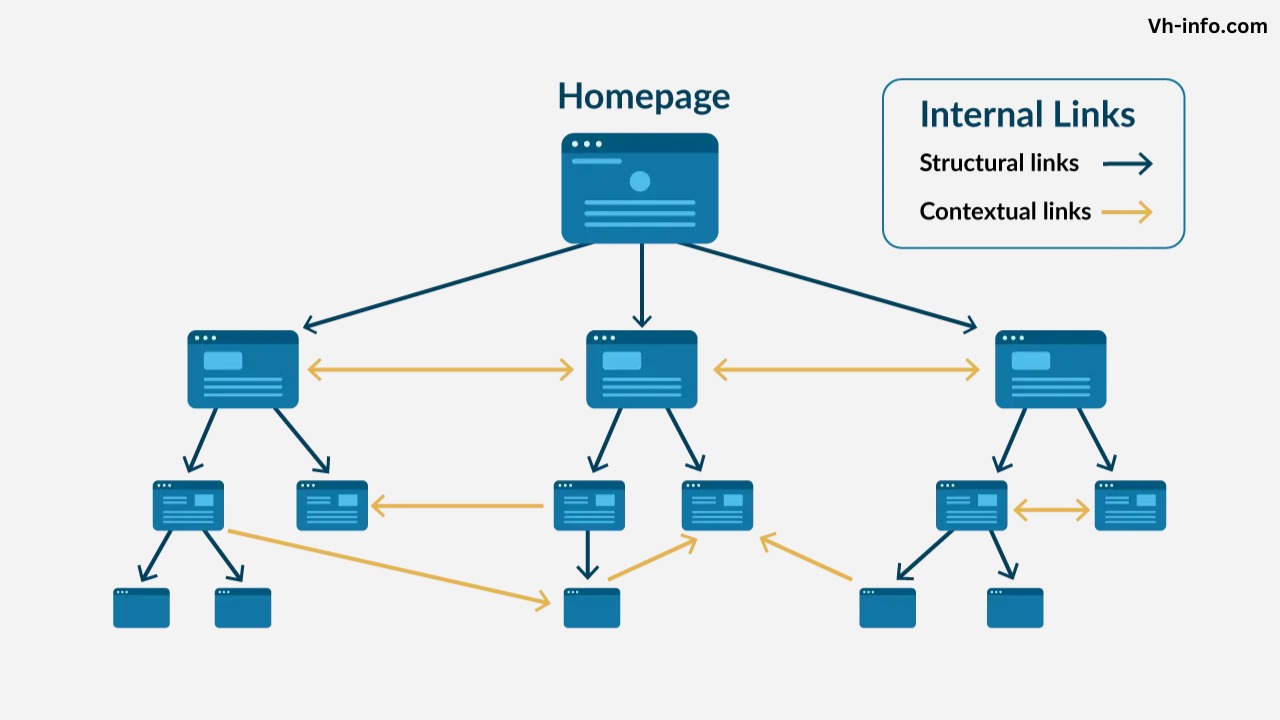
Internal linking is an important SEO strategy that helps search engines and users navigate your website.
By connecting your pages with descriptive links, you can boost your search rankings, website traffic, and user engagement.
In this ultimate guide from VH Info, we’ll dive deep into internal linking best practices and show you how to optimize your internal link structure for maximum SEO impact.
What Are Internal Links?
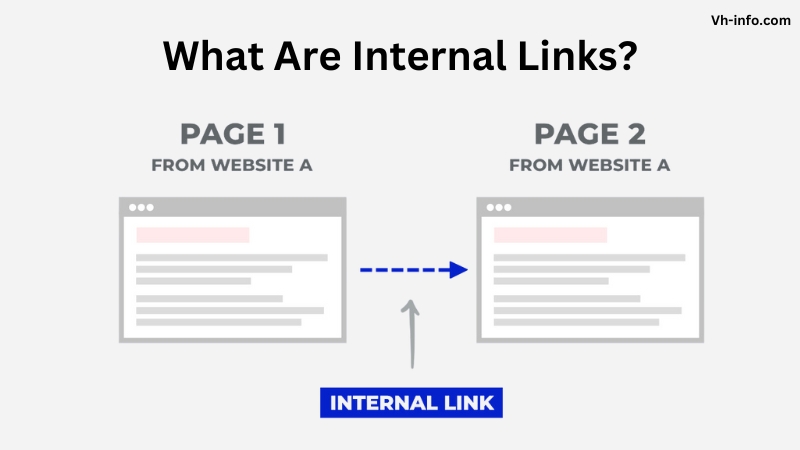
An internal link is a hyperlink that points from one page on your website to another page on the same domain. Internal links create a roadmap for search engine crawlers and help them understand your site structure and page hierarchy.
For example, let’s say you have a blog post about “SEO tips.” You could add an internal link from that post to your service page about “SEO consulting” using the anchor text “learn more about our SEO services.” This internal link transfers link equity to the target page and shows search engines and users that the two pages are related through descriptive link text.
Why Are Internal Links Important For SEO?
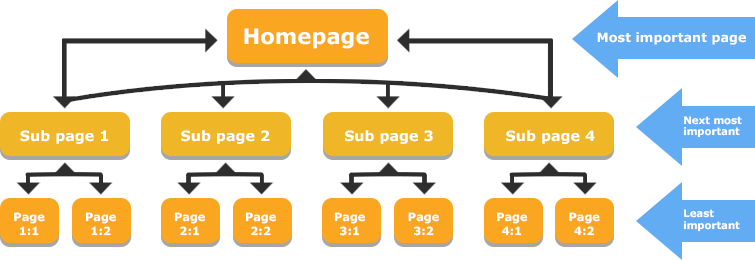
Internal links are the backbone of SEO for several reasons:
- Internal Links Establish Relationships Between Content: By linking related pages together, you show Google that your content covers a topic in-depth. This can help you rank for more keywords and establish topical authority.
- Internal Links Help Search Engines Better Find Your Content: Internal links make it easier for Googlebot to crawl and index all your site’s pages. Without internal links, search engine crawlers may miss important content.
- Link Value: When one page links to another, it passes “link juice” or link equity to the linked page. Pages with more internal links tend to have more link value, which can translate to higher search rankings.
How is it Different From an External Link?
While internal links connect pages within your site, external links point to pages on other websites. Getting high-quality external links, or backlinks is important for SEO because they act as “votes of confidence” from other sites. However, you have complete control over your internal links, making them a powerful tool for improving your site’s search performance through link building.
Internal Links Are “Super Critical” For SEO (According to Google)
When one-page links to another, it passes “link juice” or link equity to the linked page. Pages with more internal links tend to have more link value, which can translate to higher search rankings.
Types of Internal Links
There are several types of internal links you can use on your site:
- Navigational Links: The links in your site’s navigation menu help users and search engines understand your site structure. Make sure your navigation links are clear and descriptive.
- Breadcrumb Links: Breadcrumb links show the path to a page, like Home > Blog > Category > Post. They make it easy for users to jump to higher-level pages.
- Footer Links: Your footer is a great place to link to important pages like your About, Contact, and Service pages. Just don’t overdo it with too many footer links.
- Sidebar Links: Sidebar links can highlight your most popular or recent content. They’re best used sparingly to avoid distracting from your main content.
- Anchor Links: Anchor links let users jump to specific sections on the same page. They’re useful for long-form content and enhancing user experience.
- Contextual Links: Contextual internal links are placed within your page copy and surrounded by relevant text. They carry the most SEO value because they drive targeted traffic and show search engines how pages are related.
- Structural Links: Structural links are part of your site’s architecture and hierarchy, like links in your navigation and categories. They ensure all your important pages are linked together.
How Do Internal Links Affect SEO?

Internal links impact SEO in a few key ways:
- They help search engines understand your site structure and topic hierarchy.
- They distribute link equity (PageRank) throughout your site, boosting page authority.
- They guide users to related content, increasing engagement and reducing bounce rate.
- They help establish contextual relevance for keywords and topics.
How to Build Your Internal Linking Strategy?
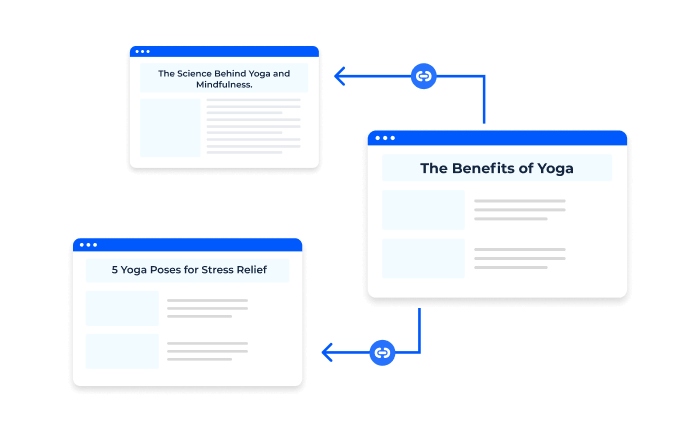
Now that you know why internal links matter for SEO, here’s how to create an effective internal linking strategy:
- Identify Your Site’s Pillar Pages: Pillar pages are your site’s most important, high-level pages that cover a core topic. Examples include your homepage, service pages, and cornerstone content. Your internal linking strategy should focus on directing link equity to these key pages.
- Create Topic Clusters Using Internal Links: Organize your content into topic clusters by linking related pages together. For example, if you have a pillar page about “Content Marketing,” link to it from blog posts covering subtopics like “blogging tips,” “SEO copywriting,” and “content distribution.”
- Choose the Right Anchor Text: When adding internal links, use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text. Instead of generic phrases like “click here,” use anchor text that describes the linked page, like “learn SEO best practices.” This helps both users and search engines understand what the linked page is about.
- Support Your New Pages: Whenever you publish a new page or blog post, make sure to add internal links from relevant, existing content. This helps search engines find and index your new content faster, while also distributing link equity to it.
SEO Benefits of Internal Linking
Effective internal linking can drive major SEO results:
- Easier for Google to Crawl and Discover New Pages: Internal links create pathways for search engine crawlers to find all your site’s pages, ensuring your content gets indexed.
- Signal Relevance and Context: By linking related pages together with descriptive anchor text, you show search engines that your content is relevant and comprehensive for particular topics. This can help you rank higher for target keywords.
- Distribute PageRank: Internal links spread link equity, or PageRank, from your most authoritative pages to other key pages. Pages with more internal links pointing to them tend to rank higher.
- Help Google Understand Your Authority on a Topic: When you cover a topic in-depth and link related content together, search engines view your site as an authority on that subject. This can lead to better rankings for a wide range of keywords.
Internal Linking Best Practices
Follow these best practices to get the most SEO value from internal linking:
- Link To and From Content-Heavy Pages: Focus on adding internal links to and from pages with substantial, valuable content, like blog posts and articles. Avoid stuffing links into thin, low-quality pages.
- Create Text Links Using Anchor Text: Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text for your internal text links. Avoid using images as internal links, as search engines can’t understand the context.
- Add an Appropriate Number of Links Per Page: While there’s no strict rule, aim for a reasonable number of internal links on each page. Stuffing in too many links can look spammy and dilute the SEO value. Aim for a few links per page, where relevant.
- Update Old Articles With New Internal Links: While there’s no strict rule, aim for a reasonable number of internal links on each page. Stuffing in too many links can look spammy and dilute the SEO value. Aim for a few links per page, where relevant.
- Add Links Where It Makes Sense: Only add internal links where they fit naturally in your content. Avoid shoehorning in links just for SEO purposes, as this can hurt readability and user experience.
- Only Add Dofollow Links: Make sure all your internal links are “dofollow” links that pass link equity. Avoid using “nofollow” tags on internal links, as this prevents PageRank from flowing.
- Take Site Navigation and Information Architecture Into Consideration: Your site’s navigation and architecture play a big role in internal linking. Make sure your navigation is clear and organized, and that every important page is reachable within a few clicks.
- Create High-Quality Content: The best internal linking strategy starts with creating linkable content. Focus on publishing comprehensive, valuable, engaging content that naturally earns links from other pages.
Common Internal Link Problems & How to Fix Them?
Watch out for these common internal linking issues that can hurt your SEO:
- Broken Internal Links: Broken internal links lead to 404 error pages, creating a poor user experience and wasting link equity. Regularly check for broken links using tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs and fix them by updating the URLs or removing the links.
- Too Many Internal Links: Stuffing too many internal links on a page can dilute their SEO value and look spammy. Stick to a reasonable number of links per page and only link where relevant.
- Nofollow Attributes in Internal Links: Using “nofollow” tags on internal links prevents them from passing link equity. Make sure your internal links are “dofollow” so PageRank flows freely.
- Orphaned Pages: Orphaned pages have no internal links pointing to them, making them hard for search engines and users to find. Identify orphaned pages by looking for pages with zero internal links in your sitemap or analytics. Add relevant internal links to these pages from other related content on your site.
- Pages With Only One Incoming Internal Link: Pages with just one internal link pointing to them may not get enough link equity. Add a few more internal links from relevant pages to boost their authority.
- Crawl Depth of More Than Three Clicks: Pages that are more than 3 clicks away from your homepage may not get crawled and indexed frequently. Adjust your site architecture to make sure all important pages are within 3 clicks of your homepage.
- Internal Redirects: Having too many internal links pointing to redirect pages can slow down page load time. Update internal links to point directly to the final URL.
- Redirect Chains & Loops: Redirect chains and loops occur when there’s a sequence of redirects between pages. This wastes crawl budget and link equity. Remove any redirect chains and point internal links to the final destination page.
- Links on HTTPS Pages Lead to HTTP Pages: If you have an HTTPS site, make sure your internal links also point to HTTPS URLs. Linking to insecure HTTP pages can cause security warnings and hurt user experience.
How to Audit Your Site’s Internal Links For Issues?
Here’s how to check your internal linking health and spot issues:
- Fix Broken Internal Links to Reclaim Authority: Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to crawl your site and identify broken internal links. Update or remove these links to reclaim lost link equity and improve user experience.
- Fix Orphan Pages: Identify pages with no internal links by analyzing your sitemap or using Google Analytics. Add relevant internal links to these orphaned pages from other pages on your site to help search engines and users discover them.
- Identify Opportunities For New Internal Links: Analyze your pages to find those with the highest authority and relevance. Look for opportunities to naturally add internal links from these pages to other important pages on your site to spread link equity and improve rankings.
Internal Links Example
Here’s an example of how you might add internal links to a blog post about “SEO tips“:
“To improve your search rankings, make sure to optimize your title tags and meta descriptions. You should also build high-quality backlinks from other relevant websites. Finally, don’t forget about on-page SEO factors like header tags and image alt text.”
In this example, the phrases “optimize your title tags,” “build high-quality backlinks,” and “on-page SEO” could be turned into internal links pointing to other relevant blog posts or pages on your site.
FAQ’s:
What is Internal Linking Vs External Linking?
Internal linking connects pages within your website, while external linking points to pages on other websites.
Are Internal Links Backlinks?
No, internal links are not considered backlinks. Backlinks are external links from other websites pointing to your site.
How Many Internal Links Are Too Many?
There’s no set rule, but having 100s of internal links on a page is likely too many. Aim for a reasonable number of links per page, based on the content.
How Many Internal Links Per Page SEO?
While there’s no strict limit, a good rule of thumb is to have no more than 100 internal links per page for SEO purposes. However, the key is to only add internal links where relevant and valuable for users.
How Do You Find Internal Linking Opportunities?
To find internal linking opportunities, start by identifying your most important and relevant pages. Look for keyword phrases in your existing content that you can turn into internal links pointing to these key pages. Whenever you publish new content, review your older related posts and pages to find natural opportunities to link to your new piece.
How Many Internal Links Should I Include Per Post?
There’s no magic number but aim for at least 2-3 internal links per post, where relevant. The key is to link naturally and not overdo it.
Can Internal Linking Affect My Site’s Load Time?
Having too many internal links on a page can potentially slow download time. Stick to a reasonable number of links and avoid linking to redirect pages.
Should I Add Internal Links to My Pages With More or Less Traffic?
Add internal links from your high-traffic, authoritative pages to other important pages you want to boost. This passes more link equity and drives targeted traffic.
How Often Should I Review My Internal Linking Structure?
It’s a good idea to audit your internal links at least every few months.
Are There Any Tools to Automate Internal Linking?
While some plugins can automatically add internal links, it’s best to manually add links to ensure they’re relevant and placed naturally.
How Do I Prioritize Pages For Internal Linking?
Focus on adding internal links to and from your most important pages, like your homepage, service pages, and cornerstone content.
Is Internal Linking Worthwhile Even on Small Sites?
Yes, internal linking is important for SEO on sites of all sizes. Even if you only have a handful of pages, linking them together helps search engines understand your content and site structure.
Conclusion
Internal linking is a powerful SEO strategy for businesses of all sizes. By connecting your pages with relevant, descriptive internal links, you can boost your search rankings, organic traffic, and conversions. Use this guide to optimize your site’s internal linking structure. With a strong internal linking foundation, you can outrank your competitors and drive more revenue for your business.