Imagine the internet is a giant library. In this library, there are billions of books. These books are websites. Now, how do you find the best book? In a normal library, you might ask a librarian. On the internet, you use a search engine like Google.
But how does the search engine know which book is the best? It looks for clues. The biggest clue is a link. When one website connects to another, it is called a link. These are also known as backlinks.
If many people point to a specific book and say, “This is great,” you will trust that book more. This is how the history began. It is a story about how the internet learned to organize information.
At VH-info, we know a lot about this. We are a SaaS link-building agency. We help companies get good links to their websites. We do not use software to trick the system. We use our brains and hard work. To be good at link building today, we must look at the past.
In this article, we will look at the full backlinks history. We will see how links started as simple connectors and became the most important ranking factor for Google search. We will look at the digital landscape and how it has changed.
The Dawn of Search: Where Backlinks History Begins
Long before Google was famous, the internet was very different. It was smaller and quieter. There were no complex search engine results. People just wanted to connect pages. This is where the story of backlinks’ history starts.
The Concept of Hyperlinks Before Search Engines
In the early days, a link was just a bridge. It was called a hyperlink. The creator of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee, wanted a way to connect documents. Think of it like a tunnel. You are reading a paper on one computer. You click a blue underlined word.
Suddenly, you travel through a tunnel to another paper on a different computer. This was magic. At this time, nobody cared about search engine optimization (SEO). There were no SEO professionals. A site owner would add external links just to be helpful.
If a scientist wrote a paper, they would link to another scientist’s research. It was honest. It was about sharing knowledge. The types of links were simple. They were mostly internal links (connecting pages on the same site) or links to friends. The digital space was built on trust.
RankDex and the Initial Idea of Link Analysis
Most people think Google invented the idea of using links to rank pages.
But in backlinks history, another man had the idea first. His name was Robin Li. In 1996, Robin Li created a system called RankDex. He looked at the linking site and the page it pointed to. He thought, “If a page has many links pointing to it, it must be good.”
He also looked at something called anchor text. This is the clickable text in a link. For example, if the blue text says “best pizza,” the page it links to is probably about pizza. This was a huge step in backlink analysis. RankDex was the grandfather of modern search.
It showed that backlink data could tell us what a webpage was about. This was the seed that grew into the world of SEO.
Why Links Were Originally Created?
Why did we start linking? It was not for Google’s algorithm. It was for people.
- Navigation: Links helped people move around the web. Without links, you would have to type a long address for every page.
- Citations: Just like in a school report, you need to show where you got your facts. Incoming link sources proved you were telling the truth.
- Recommendations: A linking website was saying, “Hey, go look at this. It is cool.”
In the early backlinks history, links were pure. They were votes of confidence. Today at VH-info, we still believe this. A link should be helpful. It should lead to valuable content. When we build links for our clients, we focus on this original purpose.
The PageRank Revolution in Backlinks History
Then, everything changed. Two students at Stanford University had a big idea. This part of backlinks history is where the modern search engine was born.
How Larry Page and Sergey Brin Changed the Game
Larry Page and Sergey Brin were the founders of Google. They looked at the web and saw a mess. Early search engines like Yahoo or AltaVista were not very smart. They only looked at the words on the page. If you wrote “cat” 100 times, you would show up first for “cat.”
Larry and Sergey built a new system. They called it BackRub at first. Later, it became Google. They used a math formula called the PageRank algorithm. This algorithm looked at the importance of backlinks. It treated the web like a popularity contest.
But it was a smart contest. It did not just count the number of links. It looked at who was linking.
The “Vote of Confidence” Methodology
Imagine you are running for class president. You need votes.
- If a random stranger votes for you, that is nice.
- If the school principal votes for you, that is amazing.
The PageRank algorithm worked the same way. A link from a small blog was a small vote. A link from a big newspaper was a big vote.
These were votes of confidence. When a high-quality site links to you, it passes page authority to your site. This made your search engine rankings go up. This was the core of backlinks’ history. It made Google the best place to find things. At VH-info, we explain this to our clients often. You do not need a million bad links. You need links from authoritative sites. That is what moves the needle.
Quantity Vs. Quality in the Early 2000s
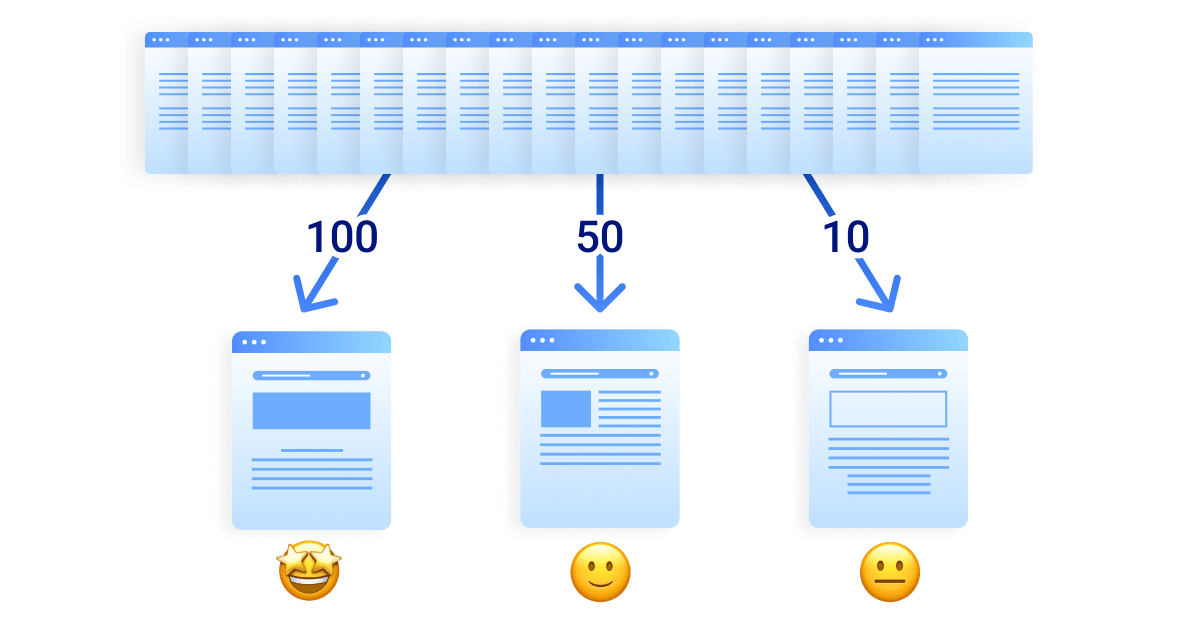
In the beginning, Google was smart, but not perfect. It still cared a lot about the total number of backlinks.
If Site A had 10 links and Site B had 100 links, Site B usually won. It did not matter if the links were great. It just mattered that there were many of them. This created a rush. Every site owner wanted more links. They did not care about link quality.
They just wanted to boost their number of backlinks. This led to a crazy time in backlinks’ history. We call it the Wild West.
The “Wild West” Era of Backlinks History (2000–2011)

From the year 2000 to 2011, the internet was like a town with no police. SEO professionals found ways to trick Google. They knew that backlinks history showed links were powerful. So, they made fake ones.
The Rise of Link Farms and Directory Spam
People created websites that had no good reading material. These were called link farms. A link farm is a group of websites that all link to each other. Imagine a group of people in a circle. Each person points to the person next to them and says, “He is famous.”
But nobody outside the circle knows them. This is how link farms worked. They also used directories. A directory is a list of websites. People would submit their site to thousands of directories. These were spammy links. They provided no SEO value to a real human.
But for a while, they tricked the search engine.
Buying Links and Black Hat Tactics
Some people did not want to work hard. They used “Black Hat” tactics. This means breaking the rules.
They would pay other websites to link to them. They would hide links in the background where you could not see them. They would use software to leave comments on thousands of blog post pages. The comments would say things like, “Great post! Visit my site.”
These were inbound link strategies that were very bad. It made the backlink profile of a site look messy.
The Abuse of Exact Match Anchor Text
Do you remember anchor text? That is the clickable word.
In this era, people abused it. If they wanted to rank for “cheap shoes,” they would make thousands of links that said exactly “cheap shoes.” This looked very fake. Normal people do not write like that. Normal people write “click here” or “check this website.”
But the search engine results rewarded this behavior. At VH-info, we look back at this time and shake our heads. It was a time of quantity over quality. But we know that shortcuts do not last forever.
The Turning Point: Algorithm Updates in Backlinks History

Google realized that people were cheating. The search results were getting bad. You would search for a dog trainer and get a spam site. Google had to fix this. This is the most dramatic part of backlinks’ history.
The Google Penguin Update (2012) Explained
In April 2012, Google launched a major update. They named it Penguin.
Penguin was like a strict teacher. It looked at the backlink profile of websites. It looked for those link farms and paid links.
If Penguin saw that you had bad links, it punished you. Your website would disappear from the google search results. Overnight, businesses lost all their visitors. It was a huge shock to the digital marketing world.
This update proved that link quality was more important than the number of links. It killed the link farms.
The Introduction of Manual Penalties
Robots are smart, but humans are smarter. Google hired real people to look at websites. These were manual reviewers.
If a reviewer saw that you were buying links, they would give you a manual penalty. You would get a message in google search console. It would say, “We found bad links. Fix them, or you stay hidden.”
This forced SEO professionals to clean up their act. They had to look at their historical data. They had to remove bad links.
How the “Nofollow” Attribute Changed the Landscape?
Google also gave webmasters a tool called “Nofollow.”
Sometimes, you link to a site, but you do not want to give it a “vote.” Maybe it is a paid ad. Maybe it is a comment section.
You can add a tag to the link code: rel=”nofollow”. This tells Google, “I am linking to this page, but I do not vouch for it.”
This changed backlinks history. It allowed sites to link freely without worrying about passing bad votes. It helped clean up the link metrics. Now, we have other tags too, like “sponsored” or “UGC” (user generated content).
Modern Link Building Vs. Backlinks History

Today, things are very different. The tricks from 2010 do not work. At VH-info, we practice modern link building. We focus on what works now.
The Shift from Quantity to Relevance and Authority
Now, you cannot just get a link from anywhere. It must be relevant. If you sell car parts, a link from a cooking blog does not help much. Google knows that cooking and cars are not related. You need a link from a car blog or a mechanic’s website.
Relevance is key. Also, authority matters. A link from a big news site is worth 1,000 links from small blogs. The SEO performance of your site depends on these high-quality connections.
We use SEO tools like Majestic SEO, Ahrefs, or Link Explorer to check these metrics. We look at page authority and trust flow.
The Role of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
Google has a new guide called E-E-A-T. It stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
Your content must show these things. And your backlink profile must support it.
- Do experts link to you?
- Do trustworthy sites mention you?
This is why digital pr is so popular now. It is about getting real news sites to talk about you. It builds trust. VH-info helps SaaS companies build this trust by getting natural backlinks from real, working websites.
Predicting the Future: AI and Linkless Mentions
What comes next in backlinks history?
Artificial intelligence is changing everything. Search engines are getting smarter. They might not always need a clickable link to know you are popular. If a famous person mentions your brand name in a video or a text, Google might count that. This is called a “linkless mention.”
Also, AI can read content better. It can tell if a link is truly helpful or just placed there for SEO. The future of SEO is about being genuinely useful. Content marketing must focus on answering questions, not just stuffing keywords.
FAQ’s:
When Did the History of Backlinks Actually Start?
The backlinks history started with the invention of the World Wide Web in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee. However, using links as a vote for ranking started with RankDex in 1996 and became famous with Google in 1998.
Why Has the Value of Backlinks Changed Throughout History?
The value changed because people tried to cheat. At first, any link was good. Then, bad actors made spammy links. So, search engines had to change to value quality over quantity. Now, SEO value comes from trust and relevance.
What Was the Most Significant Update in Backlinks History?
The Google Penguin update in 2012 was likely the most important. It stopped the “Wild West” era. It forced everyone to stop using black hat tactics and focus on valuable content. It shaped the modern digital landscape.
Are Backlinks Still As Important Today As They Were In History?
Yes, they are still one of the top ranking factors. However, the kind of link matters more. You need new backlinks from authoritative and relevant sites. A bad link can actually hurt you now.
How Does the “Nofollow” Tag Fit Into Backlinks History?
The Nofollow tag was introduced to fight spam. It allowed site owners to link without passing page authority. It helps keep the link profile clean and natural. It is a key part of best practices today.
Conclusion
The story of backlinks history is a story of evolution.
We went from simple blue lines connecting papers to a complex system of votes of confidence. We saw the rise of Google and Larry Page and Sergey Brin. We saw the crazy days of link farms and the strict rules of the Penguin update.
Today, we live in a world where quality, relevance, and trust are king.
Links are the streets of the internet. They guide us to the information we need. For any site owner, understanding this history is vital. It helps you avoid mistakes. It shows you that there are no shortcuts.
At VH-info, we love this history. It teaches us how to do our job better. As a SaaS Link Building Agency, we help you navigate this complex world. We build natural backlinks that stand the test of time. We use safe best practices to help your site grow.
The world of SEO will keep changing. Artificial intelligence will bring new challenges. But one thing will remain true: good connections matter. If you create great things, and people link to you, you will win.
If you need help building these connections, remember us. We are here to help you build a strong backlink profile that drives real results.



