In the vast landscape of the internet, web crawlers play an important role in helping search engines discover, index, and rank web pages.
As a SaaS company looking to improve your online visibility and drive organic traffic, understanding how web crawlers work and optimizing your website for them is essential.
In this comprehensive guide by VH-info, we’ll dive deep into the world of web crawling, explore its impact on SEO, and provide actionable insights to help you leverage crawling for your SaaS link-building strategy.
What is Website Crawling?

Website crawling is the process of systematically browsing and indexing web pages by automated programs called web crawlers or bots. These crawlers, also known as search engine crawlers, follow hyperlinks from one page to another, gathering data about the content, structure, and other elements of the websites they visit.
This collected data is then used by popular search engines like Google, Bing, and Amazon to build their index and determine the relevance and ranking of web pages for specific search queries.
What is a Web Crawler or Bot?
A web crawler, also known as a website crawler or bot, is a software program designed to automatically traverse the internet and gather information from websites. These bots, also referred to as web spiders, are typically operated by search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo to discover new web pages, update their existing index, and analyze the content and quality of websites.
How Do Web Crawlers Work?
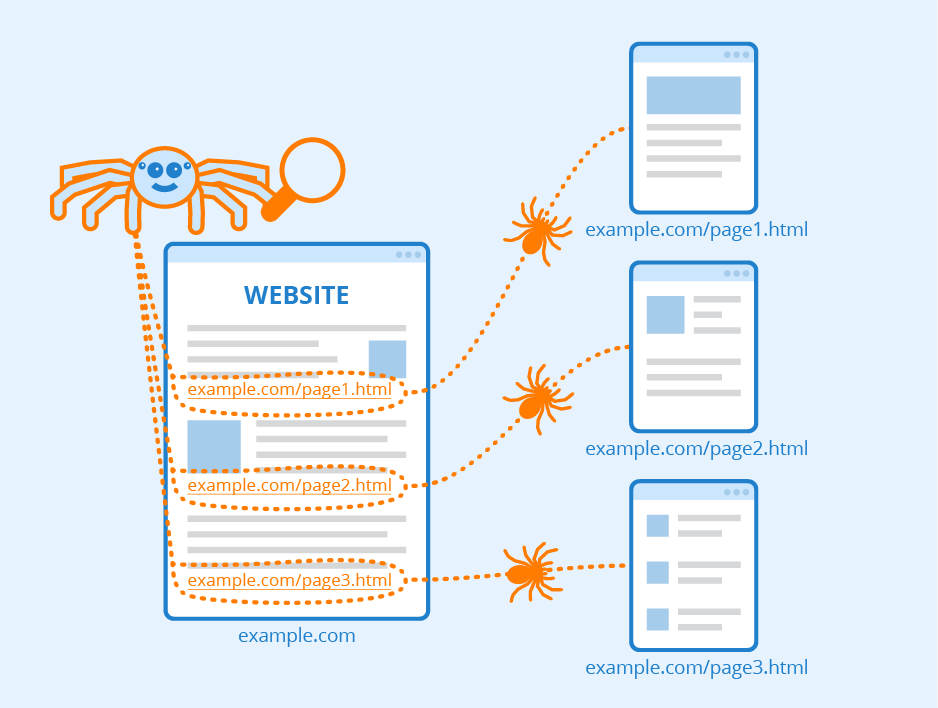
Web crawlers start with a list of seed URLs, which serve as the starting point for their crawling process. They send HTTP requests to these URLs, download the first page’s HTML content, and then extract hyperlinks to other pages. The crawlers then follow these newly discovered links, repeating the process and traversing the web like a spider navigating its web.
Robots.txt File
Website owners can use a robots.txt file to communicate with web crawlers and specify which pages or sections of their site should not be crawled. This file, placed in the root directory of a website, contains instructions that guide the behavior of crawlers.
Robots Meta Tag
In addition to the robots.txt file, website owners can use the robots meta tag within the HTMLsection of individual pages to indicate whether crawlers should index that specific page and follow its links.
Link Attributes
The “nofollow” link attribute can be used to signal to crawlers that a particular link should not pass any link equity or be followed for indexing purposes. This is useful for managing the crawl budget and preventing the indexing of low-quality or irrelevant pages.
What Types of Crawls Exist?
There are several types of web crawls, each serving a specific purpose:
- Full Crawl: A comprehensive crawl of an entire website, typically performed by search engines to build or update their index.
- Partial Crawl: A targeted crawl of specific sections or pages of a website, often used for monitoring changes or updating particular content.
- Incremental Crawl: A crawl that focuses on new or recently modified pages, allowing search engines to keep their index fresh and up-to-date.
- Site Audit Crawl: A crawl performed by website owners or SEO professionals to analyze the structure, content, and technical aspects of a website for optimization purposes.
Two Types of Web Crawlers:
Google, the world’s largest search engine, employs two main types of crawls:
- Discovery Crawl: This crawl focuses on discovering new pages and adding them to Google’s index. It follows links from known pages to uncover new content.
- Refresh Crawl: The refresh crawl revisits previously indexed pages to check for updates, changes, or any issues that may affect their ranking. This helps keep Google’s index current and accurate.
Why Are Web Crawlers Called Spiders?

The term “spider” is often used interchangeably with “web crawler” because of the way these bots navigate the internet. Just as spiders build and traverse their webs, web crawlers follow hyperlinks to move from one page to another, creating a vast network of interconnected web pages on the World Wide Web. This analogy has led to the widespread use of the term “spider” in the context of web crawling.
Why You Should Crawl Your Website?
As a SaaS company, regularly crawling your website is important for several reasons:
- Ensuring Google Crawlers Can Easily Navigate Your Site: Crawling your website enables you to detect and resolve technical issues like broken links or incorrect canonical tags that could impede Google from effectively indexing your pages. This process guarantees that your valuable content can be found and achieve high rankings in search results.
- Identifying Broken Links to Improve Site Health and Link Equity: Broken links not only provide a poor user experience but also waste crawl budgets and prevent link equity from flowing effectively throughout your site. By identifying and fixing broken links, you can optimize your site’s health and make the most of your link-building efforts.
- Finding Duplicate Content to Fix Chaotic Rankings: Duplicate content can confuse search engines and dilute the ranking potential of your pages. Crawling your site helps you identify instances of duplicate content, allowing you to take corrective actions such as implementing canonical tags or using 301 redirects to consolidate link equity and improve your search rankings.
Why Web Crawlers Are Important For Crawling Websites?
Web crawlers are the backbone of search engine optimization (SEO) as they enable search engines to discover, index, and rank web pages. Without web crawlers, your SaaS website would not be visible in search results, making it difficult for potential customers to find you.
How To Control Web Crawler Bots On Your Website?

While web crawlers are essential for SEO, there may be instances where you want to control their access to certain pages or sections of your site. Two common methods for managing crawler behavior are:
NoIndex Attribute
By adding the “noindex” meta tag to a page’s HTMLsection, you can instruct search engines not to index that specific page. This is useful for preventing the indexing of low-quality, duplicate, or sensitive content.
Disallow Directive
In your robots.txt file, you can use the “Disallow” directive to specify which pages or directories should not be crawled by bots. This helps manage your crawl budget and keeps crawlers focused on your most important content.
Web Crawling Vs. Web Scraping?

While web crawling and web scraping are often used interchangeably, they serve different purposes. Web crawling is the process of discovering and indexing web pages for search engines, while web scraping involves extracting specific data from websites for analysis or other uses. An amazon scraper, for instance, can be used to collect product prices, reviews, and other marketplace data for competitive research.
Web scraping often targets particular websites and data points, whereas web crawling is a broader, more generalized process that gathers relevant information for search engines like Google to determine a website’s SEO. To ensure stable access and avoid detection or blocking, proxies especially rotating residential proxies are almost a necessity for most modern scraping operations. Using residential proxies can help maintain anonymity and ensure uninterrupted data collection by routing requests through real user IPs. Both techniques have become increasingly important with the rise of artificial intelligence, which allows for more sophisticated data collection through web scraping and crawling.
How Do Web Crawlers Affect SEO?
Web crawlers directly impact SEO by determining which pages are indexed and how they are ranked in search results.
If your SaaS website is not properly optimized for crawling, it may not be discovered or indexed by search engines, making it invisible to potential customers.
Tools such as Google Analytics and Google Search Console can also provide valuable insights into your website’s performance and help you make data-driven decisions to improve your SEO.
How to Evaluate Your Website Crawl Data?
Analyzing your website’s crawl data provides valuable insights into its health, structure, and performance. Tools like Google Search Console and third-party site audit software can help you evaluate your crawl data and identify areas for improvement. Some key metrics to consider include:
- Crawl errors: Identify and fix any issues preventing crawlers from accessing your pages, such as server errors or broken links.
- Crawl budget: Ensure that crawlers are focusing on your most important pages and not wasting time on low-quality or irrelevant content.
- Indexation: Monitor the number of pages indexed by search engines and address any issues preventing the indexation of valuable content.
- Site structure: Analyze your site’s internal linking structure to ensure that link equity is flowing effectively and all important pages are easily discoverable.
How Do I Optimise My Website For Easier Crawling?
To make your SaaS website more crawler-friendly and improve your SEO performance, consider implementing the following best practices:
- Use a Sitemap: Create and submit an XML sitemap to help search engines discover and prioritize your most important pages. A sitemap provides a clear, structured overview of your site’s content and hierarchy.
- Improve Website Speed: Optimize your site’s loading speed by compressing images, minifying code, and leveraging browser caching. Faster loading times not only improve user experience but also make it easier for crawlers to navigate your site efficiently.
- Use Internal Linking: Implement a strategic internal linking structure to help crawlers understand the relationships between your pages and distribute link equity effectively. Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text to provide context for your links.
- Configure Robots.txt: Use your robots.txt file to guide crawler behavior and prevent the crawling of low-quality or sensitive pages. Be cautious when using the “Disallow” directive, as it can inadvertently block important pages from being indexed.
Web Crawler Examples:

Some well-known examples of web crawlers include:
- Googlebot: Google’s primary web crawler, responsible for discovering and indexing web pages for the world’s largest search engine.
- Bingbot: Microsoft Bing’s web crawler, which indexes pages for the Bing search engine.
- Slurp: Yahoo’s web crawler, used to build the index for Yahoo Search.
- Baiduspider: The web crawler for Baidu, China’s dominant search engine.
- DuckDuckBot: The crawler for DuckDuckGo, a privacy-focused search engine that emphasizes user anonymity.
FAQ’s:
Do Web Crawlers Still Exist?
Yes, web crawlers are still actively used by search engines and other entities to discover, index, and analyze web content. They are an essential component of the modern internet ecosystem.
Is it Legal to Crawl a Website?
In most cases, web crawling is legal as long as it respects the website’s robots.txt file and does not violate the terms of service or cause harm to the site. However, it’s always best to consult with legal professionals for specific guidance.
How Often Do Web Crawlers Visit Websites?
The frequency of web crawler visits varies depending on factors such as the site’s popularity, update frequency, and crawl budget. Popular and frequently updated sites may be crawled several times a day, while less active sites may be crawled less often.
How Often Should My Website Be Crawled?
The ideal crawl frequency for your SaaS website depends on how often you update your content and the size of your site. Generally, aim for at least a weekly crawl to ensure that new content is discovered and indexed promptly.
Can I Prevent Certain Pages From Being Crawled?
Yes, you can use the robots.txt file and the “noindex” meta tag to prevent specific pages from being crawled or indexed by search engines. This is useful for managing crawl budgets and keeping sensitive or low-quality pages out of search results.
Do Web Crawlers Follow Links in JavaScript Code?
Historically, web crawlers had limited ability to execute and follow links in JavaScript code. However, modern crawlers, particularly Googlebot, have become more sophisticated and can now process and follow links in JavaScript. Nevertheless, it’s still recommended to use standard HTML links for optimal crawlability.
How Can I Check if My Website Has Been Indexed By Search Engines?
You can use tools like Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools to see which pages of your site have been indexed by these search engines. Additionally, performing a site: search (e.g., site:yourdomain.com) will show you the pages that are currently indexed.
Are Web Crawlers Capable of Reading Images and Videos?
While web crawlers can detect the presence of images and videos on a page, they cannot “read” or understand the content within them. To help crawlers make sense of your visual content, use descriptive file names, alt tags, and captions.
Can Web Crawlers Access Password-Protected Content?
No, web crawlers cannot access password-protected content as they do not have login credentials. If you want search engines to index pages behind a login, you’ll need to provide alternative, publicly accessible versions of that content.
How Often Can I Change the Site Crawling Settings?
You can update your robots.txt file and meta tags as often as needed to control crawler behavior. However, be cautious when making changes, as incorrect configurations can inadvertently block important pages from being crawled and indexed.
Are There Any Free Web Crawler Tool Available?
Yes, there are several free web crawling tools available, such as Screaming Frog SEO Spider (limited to 500 URLs in the free version), Beam Us Up SEO Crawler, and Sitebulb Crawler. These tools can help you analyze your site’s structure, identify technical issues, and optimize for crawlability.
Can I Block Web Crawlers From My Website?
Yes, you can block web crawlers from accessing your website by using the robots.txt file and setting up specific rules to disallow crawling. However, keep in mind that blocking crawlers will prevent your pages from being indexed and appearing in search results, which can negatively impact your SEO efforts.
Conclusion
Web crawling is a fundamental aspect of search engine optimization, and understanding how it works is important for the success of your SaaS link-building strategy.
Optimizing your website for crawlability can enhance your search engine visibility, increase organic traffic, and ultimately expand your business.
At VH-info, we specialize in providing expert guidance and actionable insights to help SaaS companies navigate the complex world of SEO and link building.
To fully utilize your online presence and succeed in the competitive digital environment, it is important to stay updated and follow the best web crawling practices.



