With everything from our work to social life interconnected online, the risks of cyber threats loom every second.
Hackers are always looking for ways to compromise data or gain access to confidential information.
This makes cybersecurity more crucial than ever.
This article explores the importance of cybersecurity, common threats faced by ecommerce platforms, and various methods to safeguard your digital presence, ensuring that your and your users’ security is not compromised.
What is cybersecurity & why does it matter?
Everything is connected to the internet today—from our work to our social life.
However, there are people lurking in the shadows, looking for ways to swindle you by compromising your data or obtaining confidential details.
That’s where cybersecurity comes into play.
Cybersecurity involves protecting our computers, networks, and data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage. Implementing robust access control measures ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information, adding an essential layer of defense.
Imagine a world without cybersecurity. It would be like leaving your house unlocked with all your valuables inside for anyone to take. In the digital world, these valuables are your personal information, financial data, and even national security secrets. Cybersecurity is the lock that keeps these valuables safe.
And the need for cybersecurity is growing every day. According to Statista, cybercrime is expected to cost the world $13.8 trillion annually by 2025. This is a staggering amount and shows how lucrative cybercrime has become.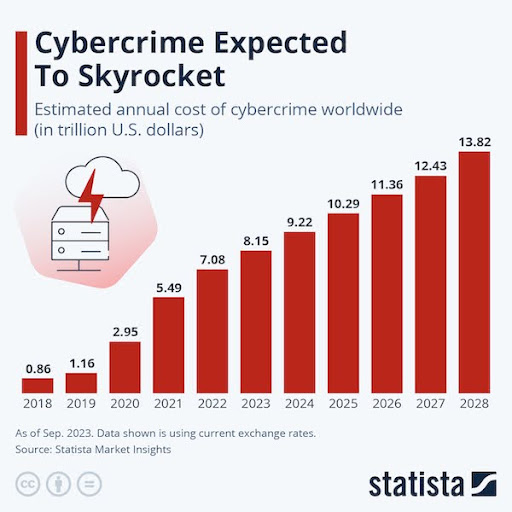 Considering the looming threat of cyber criminals, when you’re making important business decisions, cybersecurity should be at the top of your priority list.
Considering the looming threat of cyber criminals, when you’re making important business decisions, cybersecurity should be at the top of your priority list.
Cybersecurity & ecommerce
Ecommerce has revolutionized the way we shop. We can buy anything from anywhere in the world with just a few clicks.
However, this convenience comes with risks. Online stores are prime targets for cybercriminals looking to steal credit card information and personal data. To keep data secure and meet regulatory requirements, businesses can use compliance as a service and streamline their risk management processes.
For instance, consider the case of Magento, a popular e-commerce platform. In 2020, it was hit by a massive cyber attack that compromised thousands of online stores. Hackers injected malicious code on the checkout pages of Magento stores to steal payment information from unsuspecting customers. This incident highlighted the critical importance of secure and reliable hosting for Magento stores to protect customer data and ensure safe transactions.
This incident highlights just how important cybersecurity is for ecommerce stores.
Cybersecurity in ecommerce is not just about protecting against attacks—it’s also about building trust with customers. Lack of cybersecurity will leave your customers vulnerable and negatively affect your reputation. In major e-commerce markets such as China, where online retail operates at enormous scale, cybersecurity China initiatives play a crucial role in protecting both merchants and consumers.
A Cybersecurity Retail and Finance report found that 60% of consumers would stop shopping from a store that had been a victim of a cybersecurity hack. This shows that trust and proper data governance is a crucial currency in the online shopping industry.
But what are the common cybersecurity threats plaguing the industry? Let’s find out.
Common cybersecurity threats
Here are some of the most common cybersecurity threats online businesses have to look out for:
Phishing
This is like the old bait-and-switch trick. Hackers send emails that look like they’re from a legitimate source—like your bank—but they’re actually fake. They try to trick you into giving away your personal information, like passwords or credit card numbers.
For example, in 2020, a spear phishing attack on Amazon impersonated Amazon Web Services (AWS) to target users and steal their credentials.
Cybercriminals sent an email pretending to be from AWS with a link that looked legitimate but it led to a fake AWS login page.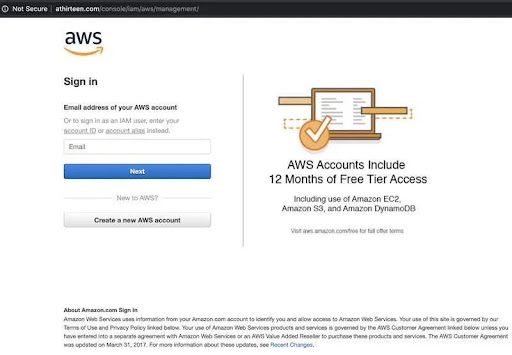 When unsuspecting users entered their login credentials, the attackers stole their information and compromised sensitive AWS data.
When unsuspecting users entered their login credentials, the attackers stole their information and compromised sensitive AWS data.
Malware
Malware—or malicious software—refers to the types of harmful software designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems.
For example, in 2019, the Emotet malware was one of the most widespread threats, causing massive damage to businesses and governments.
Some common types of malware include:
- Viruses: Programs that replicate and spread, corrupting files and causing system issues.
- Worms: Self-replicating malware that rapidly spreads across networks.
- Spyware: Software that secretly tracks users’ online activities and collects personal data.
- Trojans: Deceptive software that appears harmless but contains hidden malicious code.
- Ransomware: Malware that encrypts files or locks systems, demanding a ransom for access.
- Adware: Software that displays unwanted ads and may track browsing habits.
They can do all sorts of damage, from stealing your data to taking control of your computer.
Ransomware
Imagine if someone put a lock on your computer and asked for money to unlock it. That’s ransomware. It’s a type of malware that encrypts your files and demands payment for the decryption key.
One infamous example is the WannaCry attack in 2017, which breached the privacy of over 200,000 computers in 150 countries. Knowing about ransomware removal can prepare you to respond effectively if such an attack occurs.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks
Imagine there’s a group of hooligans blocking the entrance to a store, preventing legitimate customers from getting in. That’s what a DoS attack does to a website. It floods the site with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
A famous example is the attack on Dyn in 2016, which took down major sites like Twitter, Netflix, and PayPal.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks
This is like eavesdropping on a conversation. In a MitM attack, the hacker intercepts confidential conversations between two parties, like you and your bank, without either party knowing. They can then steal or manipulate the data being exchanged.
Types of cybersecurity methods
We use locks and security systems to protect our homes from burglars. But how do we protect ourselves from online thieves and burglars who are always looking for a way to swindle online businesses?
Luckily, there are comprehensive cybersecurity services to help you safeguard your digital presence.
Another emerging and powerful tool in combating digital threats is an artificial intelligence strategy, which goes beyond traditional antivirus or firewall protections. By integrating AI-driven solutions, businesses can automate threat detection, predict vulnerabilities based on real-world data, and streamline their responses to potential attacks. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and professional services are already leveraging artificial intelligence strategies to not only improve security but also add business value through operational efficiency and smarter decision-making. Organizations looking to develop or enhance their cybersecurity frameworks may benefit from reviewing practical examples of how AI strategy drives business value across different sectors.
1. Antivirus software
This is like having a digital doctor who checks your computer for viruses and other malware.
Antivirus software scans files and programs to detect and remove malicious software, perform secret scanning, or malware from your system. It’s your first line of defense against cybercriminals with nefarious intentions.
Some well-known antivirus providers include Norton, McAfee, and Kaspersky.
2. Firewalls
A firewall checks all the data coming in and going out, and if something doesn’t follow the rules, it blocks it to keep your network safe.
Think of it as a security guard for your computer network security.
Companies like Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, and Fortinet are big names in the firewall game. They’re always coming up with new ways to keep the bad guys out.
3. Encryption
Encryption is like a secret code for your digital information. It transforms readable data into a scrambled format, and only parties that have the key to decode it can access it.
Here’s how it works in action:
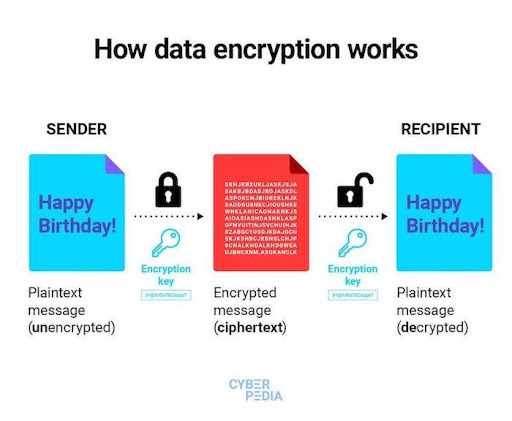 This is crucial for protecting sensitive information from prying eyes—now more than ever, when online data leaks are prevalent.
This is crucial for protecting sensitive information from prying eyes—now more than ever, when online data leaks are prevalent.
Most online social media and messaging platforms, such as WhatsApp and Snapchat, claim to keep your information encrypted, which allays any doubts their users might have about privacy concerns.
Hashing is another encryption technique. It transforms data into a fixed-size hash value or digest, which acts like a digital fingerprint. That said, hashing is a one-way process, meaning you can’t reverse the hash value to get the original data. This makes it ideal for securely storing passwords.
Major encryption companies include Symantec, McAfee, and RSA. These companies provide a range of encryption solutions to protect data for individuals, businesses, and governments.
4. Two-factor authentication
We usually have double locks on our door to keep potential intruders and burglars out.
In the digital world, we have two-factor authentication (2FA) that adds an additional security layer to your online profiles and accounts by requiring two different types of verification before you can log in. It’s like needing both a key and a fingerprint to unlock a door.
Here’s how it works:
- Start by entering something you already know: This is usually your password. It’s the first layer of security.
- The next step is to add something you have: This could be a code sent to your phone, a fingerprint, or a physical token. It’s the second layer of security that makes sure it’s you trying to log in.
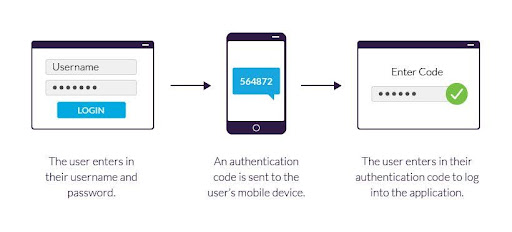 Some examples of 2FA methods include:
Some examples of 2FA methods include:
- SMS Verification: After you enter your password, you’ll receive a code on your mobile phone.
- Authentication Apps: Apps like Google Authenticator generate time-sensitive codes or time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) that you use to log in.
- Hardware Tokens: These are physical devices that generate codes or use biometrics (like fingerprints) for authentication.
- Push Notifications: You get a notification on a trusted device, and you approve the login attempt from there.
These 2FA methods especially come in handy for businesses related to banking or financial services marketing.
5. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Intrusion Detection Systems are cybersecurity platforms that monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and potential cybersecurity threats.
They analyze this data to identify patterns or behaviors that may indicate a cyber attack or unauthorized access. When an IDS detects a potential threat, it will raise the alarm so that the system administrator or security personnel can take appropriate action to prevent a data breach. For even stronger internal protection, implementing advanced insider threat detection solutions helps organizations uncover risks from within — whether accidental or malicious — before they escalate into critical security breaches.
How to build your cybersecurity defense to keep you & your users secure
Leveraging cybersecurity methods to circumvent digital threats isn’t enough. With the ever-increasing online scammers, you have to make your business extra secure to prevent security threats.
You need to build a strong cybersecurity defense to keep you and your clients secure.Here are some quick ways to help you do that:
- Use Strong Passwords: Your password should be strong and unique enough that no one will be able to guess it. Use special characters and a mix of numbers, lower case, and upper case to make it long, complex, and unique. Consider using a password manager to keep track of them.
- Keep Software Up to Date: Cybercriminals are always looking for ways to exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Make sure you regularly update all the software you use in your workspace. From your CRM to SEO tools, updates can patch these holes and keep attackers out.
- Educate Your Team: Make sure everyone in your team knows the basics of cybersecurity. Regular training can help prevent accidental breaches.
- Back-Up Your Data: This is like having insurance. Regularly back up your data so that you can recover it in case of a cyber attack.
- Have an Incident Response Plan: What if a break-in occurs despite all the security measures in place? Always be prepared for the worst, so you can minimize damage and recover quickly.
- Implement Secure QR Code Practices: Ensure QR codes are securely generated and educate users on safely scanning them to avoid directing to malicious sites or initiating unwanted downloads.
- Set Up DMARC Protocol: By setting up the DMARC protocol and using a DMARC checker to verify it, you ensure that only authorized senders can use your domain for email communication, adding an extra layer of security and enhancing your brand’s trustworthiness.
Conclusion: Stay on top of cybersecurity threats
We talked about the importance of cybersecurity in protecting against common threats like phishing, malware, and ransomware, especially for ecommerce platforms.
We also discussed ways to sidestep these issues using cybersecurity methods like antivirus software, firewalls, encryption, 2FA, and intrusion detection systems.
As you look to build and strengthen your brand securely, keeping security threats at bay, consider leveraging resources like VH-Info. They offer insights and solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring your marketing and cybersecurity efforts are top-notch.


