Running a dropshipping business lets you launch an online store with lower upfront costs and no warehouse space. As a business model, dropshipping handles order fulfillment through reputable suppliers who ship products directly to customers.
But what about legal compliance? This guide breaks down complex legal issues around dropshipping, so you can build a legitimate business, meet tax obligations, and offer exceptional customer service.
What Is Dropshipping?
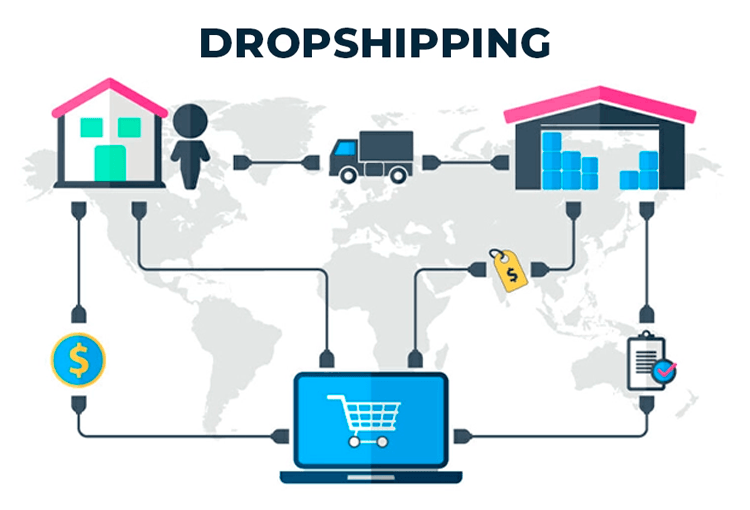
Dropshipping is an ecommerce model where the seller of record lists products on their dropshipping store but never holds inventory. When a customer places an order, the store forwards order processing to reliable suppliers, who handle product quality control, packing, and shipping times. This supply chain approach reduces upfront costs and lets entrepreneurs focus on marketing, social media, and customer experience.
How Dropshipping Works?
- You set up an online store on e-commerce platforms like Shopify, Amazon, eBay, Etsy, or Walmart.
- You select products from verified dropshipping suppliers or marketplaces such as AliExpress.
- You create product descriptions highlighting product safety standards, intellectual property rights, and shipping costs.
- A customer places an order and pays sales tax if required.
- You forward the customer orders to your supplier, pay the wholesale price, and handle income tax through tax professionals.
- The supplier ships the product directly to your customer. You provide ongoing customer support and manage returns or disputes according to your terms of service.
Is Dropshipping Legal?

Dropshipping is a legitimate business when you follow consumer protection laws, intellectual property requirements, and data protection regulations. You are the seller of record, so you hold legal liability for product liability insurance, accurate product descriptions, and compliance with Federal Trade Commission rules and local tax laws. Failure to register your business or collect sales tax can lead to legal risks and penalties.
Legal Requirements For Dropshipping

Dropshipping businesses must follow some legal requirements, which are as follows:
Copyright Laws
Dropshippers must avoid using copyrighted images, text, or trademarks without permission. Always get a license or written agreement from the original creator before you use product descriptions or photos.
If you sell counterfeit goods or copy another brand’s intellectual property, you risk fines, account suspension, and legal liability for infringing on intellectual property rights.
Protect your dropshipping store by working with reputable suppliers and creating original product descriptions.
Consumer Protection and Product Safety Laws
You are responsible for offering safe products that meet consumer protection laws.
In the United States, the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) enforces safety standards and can require recalls of defective products. You must display clear return policies, refund terms, and consumer protection clauses in your privacy and returns policies.
Failing to meet product safety standards or misleading customers about product quality can lead to penalties, lawsuits, and damage to your dropshipping venture.
Truth in Advertising Laws
Advertising must be truthful and not misleading under the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Act. Claims like “fast shipping” or “premium quality” must match your actual service and product performance. You need evidence to back up every claim. Omitting key details—such as longer shipping times—can be deemed deceptive marketing and expose you to fines and FTC enforcement actions.
Tax and Licensing Laws
Before you launch your dropshipping business, register it with local and state authorities and obtain any required business license.
You must collect and remit sales tax in all regions where you have nexus—this could be where you live, where your suppliers are, or where your customers are located.
Income from your dropshipping store is subject to income tax, and you should consult tax professionals to handle tax obligations, GST (in India), VAT (in the EU), and other tax requirements.
Platform-Specific Requirements
Each ecommerce platform—Amazon, eBay, Etsy, Walmart, Shopify—has its own rules for dropshipping sellers.
For example, Amazon requires you to be the seller of record and manage customer service, while Etsy only allows handmade, custom, or vintage items. Violating platform terms of service can lead to account suspension or permanent bans, so review and comply with each platform’s dropshipping policies and seller guidelines.
Data Protection Laws
Dropshipping stores collect personal data such as names, addresses, and payment details. You must comply with data protection regulations like GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), CPRA, and other state and federal privacy laws.
Implement strong security measures, clear privacy policies, and allow customers to access, delete, or opt out of data collection. Non-compliance can result in significant fines and loss of customer trust.
Food, Drugs, and Alcohol Regulations
If you sell consumables, cosmetics, or supplements, comply with Food and Drug Administration (FDA) rules and local health regulations.
Products like cosmetics must meet FDA good manufacturing practice (cGMP) requirements, proper labeling, and ingredient safety substantiation under MoCRA. For food or alcohol, follow the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and display any necessary certifications, warnings, or age restrictions. Violations can lead to recalls, penalties, and criminal charges.
Anti-Money Laundering Regulations
Your dropshipping business should use anti-money laundering steps. These steps help check customer identities and watch for strange deals.
In the U.S., FinCEN asks for ownership info from some businesses. Worldwide, you need to follow AML rules and check for sanctions in deals and suppliers. Good AML practices lower legal risks. They also help reduce crime related to money.
Sanctions Compliance
Always check suppliers and customers against international sanctions lists. Do not get products from or send to countries with trade bans. Breaking these rules can result in large fines. It can also lead to shipping limits and harm your business image.
Use trusted tools for sanctions compliance. Talk to legal experts to keep up with banned areas and groups.
Anti-Slave Labor Regulations
Vet your suppliers to ensure they adhere to labor laws and ethical practices.
Avoid goods produced with forced labor, human trafficking, or unfair wages. International laws like the U.S. Trade Facilitation and Trade Enforcement Act prohibit importing products made with slave labor.
Including ethical practices in your supply chain not only ensures legal compliance but also builds customer trust and strengthens your dropshipping business model.
Is Dropshipping Legal Under 18?

Minors can run a dropshipping business, but you must address legal compliance and contract capacity.
In most places you need to be 18 to sign a binding contract, so under-18 entrepreneurs must have a parent or guardian co-sign as the seller of record and hold the business license and payment processors account. You can still manage product descriptions, marketing, order fulfillment, and customer service, but reliable suppliers and platforms often require adult approval for tax obligations and sales tax collection.
A guardian-backed business structure lets you focus on inventory management, dropshipping store growth, and customer support while staying within legal requirements.
Always vet reputable suppliers, set up clear terms of service, and consult legal professionals to ensure full legal compliance.
Platform-Specific Dropshipping Requirements

Following the rules of each platform is very important for a dropshipping business.
- Amazon: On Amazon, you must act as the seller of record, meaning your dropshipping store appears on all packing slips and invoices. You handle order fulfillment, customer service, and returns under Amazon’s terms of service. Always use reliable suppliers to meet shipping times and product quality standards, and ensure you have the necessary business license, tax obligations, and sales tax requirements in place to stay compliant.
- eBay: eBay requires accurate listings with clear product descriptions, shipping costs, and delivery estimates. You’re responsible for order processing, customer support, and handling returns within eBay’s seller performance rules. Maintain legal compliance by following consumer protection laws, respecting intellectual property rights, and collecting any sales tax owed in your region.
- Etsy: Etsy limits dropshipping to items that meet their handmade, vintage, or craft supply rules—generic mass-produced products aren’t allowed. You must create original product descriptions and images, or work with reputable suppliers who comply with Etsy’s intellectual property and consumer protection policies. Ensure your privacy policy and returns terms are clear, and track order fulfillment and shipping times closely.
- Walmart: Walmart Marketplace sellers need pre-approval and must submit to a rigorous supplier vetting process. You must display accurate product quality information, honor their low-price guarantee, and meet strict order fulfillment timelines. Register your dropshipping business, handle sales tax requirements, and comply with data protection laws when collecting customer details on Walmart’s platform.
- AliExpress: AliExpress is primarily a sourcing hub—dropshippers use it to find verified suppliers offering low upfront costs and a wide supply chain. You manage your own online store, set clear shipping costs and shipping times, and create compliant product descriptions to meet consumer protection laws. Always monitor product safety standards, vet suppliers for ethical practices, and handle any customer order issues directly.
Countries Where Dropshipping Is Legal Or Restricted
Legality for dropshipping is different in each country.
United States
Dropshipping is fully legal in the United States, but you must set up a proper business structure (LLC or sole proprietorship) and obtain any required business license. You’re responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax in states where you have nexus, and you must comply with federal and state consumer protection laws, including accurate product descriptions and safe product standards.
As the seller of record, you handle order fulfillment, customer support, and payment processors, and you remain liable for product liability insurance and intellectual property rights compliance
United Kingdom
In the UK, dropshipping is legal but subject to VAT and consumer rights regulations. You must register for VAT if your taxable turnover exceeds £90,000 or if you’re an overseas seller, and you need to charge 20% VAT on eligible sales.
UK consumer protection laws grant customers a 14-day right of return, and you must display clear terms & conditions, privacy policies, and refund policies on your online store. Complying with HMRC rules, data protection (UK GDPR), and platform-specific requirements (e.g., Amazon’s seller of record) is essential for legal compliance.
India
Dropshipping is legal in India, provided you register under the GST regime once your turnover exceeds ₹20 lakhs (or ₹10 lakhs in special category states).
You need a GST number to collect and remit CGST, SGST, or IGST on each sale, and you must issue proper GST invoices to customers.
Register your business (sole proprietor, partnership, or company), maintain accurate records for input tax credits, and ensure your suppliers comply with product safety and consumer protection laws.
Failure to register or collect GST can result in penalties and disrupt your supply chain.
European Union
Across the EU, dropshipping requires compliance with the Consumer Rights Directive, which gives buyers a 14-day right of withdrawal and mandates clear disclosures of delivery costs and seller identity.
You must register for VAT in each member state where you hold stock or use the One-Stop Shop (OSS) for cross-border VAT reporting. GDPR data protection rules apply to all personal data you collect, and you must adhere to product safety standards under EU regulations.
Each country may add specific consumer protection or labeling requirements, so verify local rules before selling in that market.
Other Regions
In regions like Canada, Australia, and Southeast Asia, dropshipping is generally legal but governed by local tax obligations (GST/HST, GST, VAT), import duties, and consumer protection laws.
You must register your business, collect applicable sales taxes or duties, and comply with platform-specific policies. Data protection laws (e.g., PIPEDA in Canada, Privacy Act in Australia) require clear privacy policies and secure handling of customer data.
Always vet reliable suppliers to meet product safety standards and maintain a reputable dropshipping store in each jurisdiction.
Why Start A Dropshipping Business?

Starting a dropshipping business lets you launch an ecommerce store with lower upfront costs and no need for warehouse space or large inventory. You partner with reliable suppliers who handle order fulfillment, freeing you to focus on marketing, social media, and improving customer experience.
This business model reduces shipping costs and financial risk, since you only pay for products after a customer places an order.
Managing a dropshipping store also means you can test new products quickly, fine-tune your product descriptions, and optimize your fulfillment process without tying up capital in stock.
With the right legal compliance, tax obligations, and clear terms of service, you build a legitimate business that scales easily and delivers strong customer satisfaction. Plus, you can run your dropshipping venture from anywhere, making it an online store solution perfect for flexible, growth-oriented entrepreneurs.
Legal Risks and Common Pitfalls in Dropshipping

Selling Counterfeit Or Restricted Products
Selling counterfeit goods or items that are restricted by law can lead to serious legal liability.
If your dropshipping store lists fake branded products, you violate intellectual property rights and open yourself to lawsuits and fines. Restricted products—like certain electronics, cosmetics, or items requiring special permits—may need approvals or certifications before sale.
Always work with reputable suppliers who provide proof of authenticity and ensure your product descriptions correctly reflect product quality and safety standards.
Failing to vet suppliers can damage your brand’s reputation and result in platform policy violations or account suspension.
Copyright and Trademark Infringement
Using images, text, or logos without permission risks infringing on copyright and trademark laws. When you copy another brand’s product photos or use unlicensed music or video in social media ads, you expose your dropshipping business to legal claims.
Intellectual property rights protect creators, so always create or license original product descriptions, images, and marketing materials.
Including clear terms of service and respecting copyright laws in your online store helps maintain legal compliance and avoids takedown notices or hefty fines from rights holders.
Platform Policy Violations
Each ecommerce platform enforces specific rules and terms of service that dropshippers must follow.
For example, Amazon requires you to be the “seller of record” and manage customer service, while Etsy bans mass-produced goods. Violations—such as inaccurate shipping times, misleading product descriptions, or failure to process returns—can lead to account suspension or permanent bans.
To stay compliant, regularly review platform-specific requirements, maintain clear privacy and returns policies, and ensure your order fulfillment process meets promised shipping costs and timelines.
Tax Compliance Issues
Neglecting sales tax and income tax can harm your dropshipping business. It is important to register your business. You also need to get a business license. Be sure to collect sales tax in places where you operate.
Income from your online store is subject to income tax. Laws vary in different areas, like the U.S., the EU, and India. Each region has its own rules about sales tax, VAT, or GST. Talk to tax experts to make sure you follow the laws. They can help you file returns on time and keep good records. Not following the rules can result in fines or back taxes. It can also damage your business’s good name.
How to Keep Your Dropshipping Business Legal?

To keep your dropshipping business legal,
Registering Your Dropshipping Business
Before you start selling, set up a formal business structure—such as a sole proprietorship or LLC—to meet legal requirements.
Obtain any necessary business license or seller’s permit in your jurisdiction, and register for tax purposes (for example, a VAT number in the EU or a GST number in India).
Having a registered dropshipping business ensures you can collect and remit sales tax correctly and file income tax returns. This clear business structure also helps when opening payment processors accounts and building trust with customers and suppliers.
Choosing Verified Suppliers
Work only with reputable suppliers who provide proof of authenticity, quality control measures, and transparent shipping times.
Reliable suppliers reduce the risk of counterfeit goods, product liability issues, or shipment delays that violate consumer protection laws. Ask for supplier references, certifications, and sample orders to verify product quality.
Maintaining a solid supply chain with ethical practices helps you comply with anti-slave labor regulations, food or drug rules if applicable, and keeps your dropshipping model legitimate.
Setting Up Legal Policies (Privacy, Returns, Terms & Conditions)
Draft clear, easy-to-read policies for privacy, returns, and terms & conditions and display them prominently on your dropshipping store.
Your privacy policy must explain how you collect and protect customer data under laws like GDPR or CCPA. Your returns policy should outline refund procedures, timelines, and any restocking fees to comply with consumer protection and truth in advertising laws.
Terms & conditions clarify order fulfillment processes, payment processors accepted, and dispute resolution steps—helping you avoid platform policy violations and build customer satisfaction.
Ensuring Product Safety and Liability Coverage
Make sure every product you sell meets applicable safety standards—such as CPSC rules in the United States or CE marking in the EU—and include accurate product descriptions reflecting those standards.
Carry product liability insurance to protect your dropshipping store against claims for defective or dangerous items. This insurance covers legal fees and damages if a product causes harm.
Combining safety checks with liability coverage helps you comply with consumer protection laws, manage legal risks, and demonstrate your commitment to customer safety.
FAQ’s:
Is It Necessary To Have A Business License For Dropshipping?
Most places see a dropshipping store as a retail shop. You usually need a business license or seller’s permit first. This is important before you collect payments and run an online store.
If you register your dropshipping model as an LLC or sole proprietorship, it helps with taxes. It also lets you open payment accounts and follow consumer laws. If you skip this step, you may face fines. You could also have problems with your business setup.
Additionally, there may be legal issues about product safety and your rights to ideas.
Can You Dropship Internationally Legally?
Yes, you can sell to customers worldwide, but international dropshipping brings customs regulations, import duties, and cross-border VAT or GST requirements into play. You must research each destination’s consumer protection and product safety standards, register for the EU’s One-Stop Shop (OSS) if shipping to the EU, and collect sales tax or GST where you have nexus or cross-border obligations. Failing to comply with customs or tax laws can result in held shipments, returned goods, and penalties that harm your dropshipping business model.
What Are The Penalties For Non-Compliance With Dropshipping Laws?
Penalties vary by region but can include hefty fines, forced business shutdowns, and account suspension by ecommerce platforms.
In the EU, a Dutch retailer faced a €90,000 fine for failing to disclose dropshipping arrangements and return requirements under consumer protection laws.
Tax non-compliance—like not collecting or remitting sales tax—can trigger interest charges and state audits, while violating intellectual property rights or truth in advertising laws can lead to takedown notices, lawsuits, or FTC enforcement actions.
Can Dropshipping Be Considered A Pyramid Scheme?
No. Dropshipping is a legitimate ecommerce business model where you sell physical products sourced from third-party suppliers without holding inventory. You earn a margin on each sale rather than recruiting members or charging fees for recruitment.
Unlike pyramid schemes—which rely on recruitment and promise commissions for enrolling others—dropshipping’s revenue comes solely from order fulfillment, making it a legitimate, low-risk business venture when you follow legal compliance and consumer protection laws.
Do I Have To Collect Sales Tax On Dropshipped Items?
Yes, if you have nexus—such as a business license, office, or significant sales—in a region, you must collect and remit sales tax on orders shipped there.
In the United States, over 10,000 tax jurisdictions vary by state and locality, so you need to register for sales tax permits in each state where you meet nexus thresholds.
Internationally, VAT in the EU and GST in India apply when your turnover exceeds specified limits, requiring regular filings and accurate record-keeping with tax professionals’ help.
Is Dropshipping Profitable?
Dropshipping can be profitable due to its low upfront costs, no warehouse space, and minimized inventory risk. You invest in marketing, customer support, and building your online store’s brand rather than stocking products.
Profitability hinges on choosing reliable suppliers, optimizing product descriptions, maintaining competitive pricing, and managing legal compliance and tax obligations effectively.
When executed well, this dropshipping venture allows you to scale quickly and focus on customer satisfaction and growth.
Conclusion
Dropshipping offers aspiring entrepreneurs a low-risk dropshipping business model with lower costs and no warehouse space.
Understanding legal requirements, such as consumer protection laws, tax obligations, intellectual property rights, and platform-specific regulations, helps you protect your dropshipping business while providing an excellent customer experience.
For expert SaaS link building and further actionable insights on building authority, visit VH Info and start growing your online presence today.