Search queries are at the heart of every online discovery. People type them into a search box or a search bar, hoping to get relevant results about a topic, product, or service.
For SaaS businesses and marketing teams, search queries are essential because they reveal the needs of searchers, the topics they care about, and the products they want.
Creating a strategy around this concept results in more targeted traffic, higher conversions, and better brand awareness.
At VH Info, we work with SaaS brands that want to strengthen their online presence. We see each search query as an opportunity to deliver quality content and address what users genuinely want.
Through proper optimization, it is possible to guide your target audience to landing pages that match their intentions, ultimately leading to better outcomes in search marketing.
Below, we discuss what a search query is, why it matters, how to use different types of searches to your advantage, and how to select keywords based on user queries.
What is a Search Query?
A search query is any search term or a set of words entered into a search engine to find specific information, products, or services.
Whether it is a short phrase or a detailed sentence, the search query itself represents a user’s intention—often referred to as search intent—to learn, compare, buy, or reach a particular website.
When searchers enter these terms, the search engine analyzes them to return the most relevant results.
Every search query can have different meanings, which is why search engine optimization efforts rely on analyzing query data. A query might reference a brand name, a product name, or an interest like “los angeles coffee shops.”
Each scenario reveals how vital it is to match user queries with the correct web page. If you focus on aligning your content with the intent behind these search queries, you increase the odds of appearing in the search results that matter most.
Importance of Search Queries in SEO and Digital Marketing

Search queries serve as a guide for search marketers to develop targeted strategies. By examining queries and their context, you can create content and optimize it so users find you when they need you.
This leads to:
- Improved Visibility: Having your web page show up at the right time boosts brand awareness.
- Higher Organic Search Traffic: Ranking for queries that are relevant to your specific industry can drive consistent traffic at no direct cost, aside from production of quality content.
- Better User Satisfaction: If your web page matches user intent, visitors remain on your site longer, which sends positive signals to the search engine.
- Enhanced Conversions: Aligning transactional queries with your product listings can increase the rate at which visitors take action, whether that is subscribing or purchasing.
For search marketers, mastering how people use queries also helps you refine PPC ads, improve local searches, and determine which vertical search segments might be most relevant. From a search marketing standpoint, focusing on user queries—and categorizing them properly—sets the foundation for meeting the needs of searchers.
Types of Search Queries

Many experts break down search queries into different types based on user goals.
Here are four primary categories you should be aware of when shaping your strategy:
Branded Queries
A branded query includes a brand name, such as “VH Info link building services.” Often, the user wants to locate a particular website or research a specific brand. This type of search query is valuable for brand awareness and for securing top positions in relevant results. You can appear in both organic search and PPC ads, ensuring you are the first link people see when they type your name.
Informational Queries
Informational queries, sometimes referred to as informational search queries, indicate that a user wants information. The user might be typing something like “how to start a SaaS link campaign” or “best practices for on-page search engine optimization.”
They are not necessarily looking to purchase; they are researching to find relevant information on a topic. Informational searches are common when people want advice, instructions, or details.
Creating resources that address these queries fosters trust, brand credibility, and site authority.
Navigational Queries
Sometimes labeled navigational search queries, these searches occur when a user already knows the specific website or page they want. Rather than entering a URL directly, they type the name in a search bar.
For instance, a search query like “VH Info blog” is navigational. The best way to handle navigational queries is to ensure you own the top organic search spot for your brand or name.
If people are trying to reach you by your brand name, they should see your site sitting comfortably at the top of the search results.
Transactional Queries
Transactional queries signal that the user intends to do something immediate, such as buying, signing up, or downloading. These are often called transactional search queries.
Examples might include “buy link building services,” “order new SaaS software,” or “purchase CRM tools for small businesses.”
Since transactional search indicates high conversion potential, it is wise to create product listings or landing pages that match these queries. Additionally, you can use PPC ads or google ads to capture these ready-to-buy users who are on the verge of taking an action.
How to Use Different Types of Search Queries?

Once you recognize that people use different types of searches, you can cater to each type of search query effectively. This means aligning the content and structure of your site with each user’s intentions.
Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are phrases that are more detailed and specific. They often have lower competition but higher intent.
For instance, “link building strategies for SaaS startups” is more specific than a generic phrase like “link building.” If your content focuses on these specific long-tail queries, you can attract a smaller but highly targeted audience looking for particular information.
How to Find Long-Tail Keywords?
Tools and analytics provide a starting point. You can check your own search query report in Google Search Console to see which user queries bring people to your site. Social media platforms can also reveal the types of questions people ask repeatedly in your industry.
By looking at the queries with moderate traffic or minimal competition, you can discover hidden gems that lead to higher conversions and more consistent growth.
Check the Competition
Investigate how other sites rank for key long-tail queries. Look at their on-page elements such as title tags, meta descriptions, and headings. Then include similar or improved strategies into your own content.
You can analyze their landing pages, observe whether they use images or video, and figure out what gaps you can fill. Sometimes, a competitor misses a related phrase or fails to provide relevant information to the target audience, opening the door for your site to stand out.
Difference Between Keywords and Search Queries
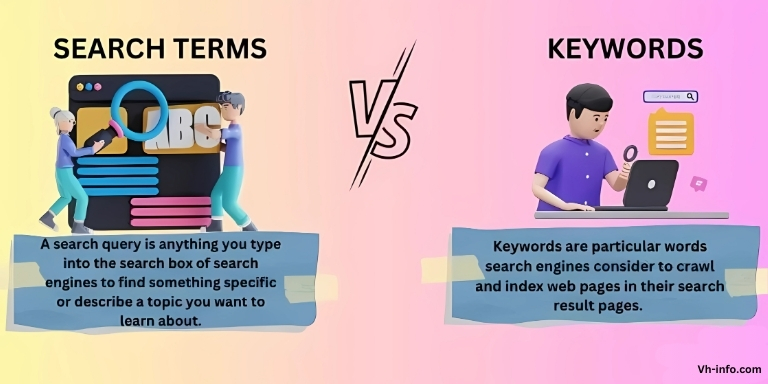
While “keywords” and “search queries” often mean the same thing, they have different roles in SEO. Knowing the difference is key for a good digital marketing plan.
Understanding Keywords
In SEO, “keywords” typically refer to the terms or topics you want your content to rank for. You research which words people use in search engines and then optimize your web page or landing pages around them.
Keywords might be short phrases like “SaaS link building” or more detailed variants like “white-hat link building strategies for SaaS companies.”
How Keywords Relate to Search Queries?
While keywords provide a focus for your optimization, search queries are the actual phrases typed into a search box.
For instance, your keyword might be “SaaS link building platform,” but a common search query type from a user could be “best SaaS link building platform in Los Angeles.”
Each user can phrase their request differently, and your SEO approach should cover these variations. If you only optimize for the base keyword, you might miss all the related user queries that contain additional details.
On the flip side, merging keywords with the precise queries users make is how you match their search intent with your content.
The more alignment there is, the more likely you are to appear in relevant results and meet user needs. That alignment leads to a win-win: the user finds the answer or product they want, and your site gains more engaged visitors.
How to Select Keywords Based On Search Queries?

Choosing the right keywords is like tuning an instrument. It takes time to understand the details of language, what users want, and how search engines work. A good keyword plan depends a lot on the data from real search queries. This data gives you helpful hints about what users are looking to find.
Identify the Search Queries that Bring Users to Your Site
Consult your data sources like Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and any search query report you have available.
Pinpoint the user queries that actually generate traffic. These might already match your core product name or brand name keywords, or they could be random questions that produce surprising visits.
By spotting which search query type yields clicks or conversions, you can see where your brand is already strong or where you might have hidden strengths.
Find New Search Queries Based On Your Current Keywords
Sometimes, your existing keyword focus might only capture the surface. You can expand by researching synonyms, variations, or related terms used by the target audience.
This might involve local searches if you serve a specific area, or it might involve vertical search terms if you operate in a specialized sector.
For example, if your main keyword is “SaaS link building,” related queries could be “SaaS link building expert,” “link building for B2B SaaS,” or “how to scale SaaS backlinks.”
Use This Information to Improve Your Keyword Strategy
Once you identify potential queries, weave them into your meta descriptions, headings, and product listings. You could also create new category pages or blog posts that address these topics directly.
For instance, if you notice that people often search “how link building works for a CRM tool,” launching a dedicated blog post to answer that specific information can yield a valuable traffic source.
This approach helps your SEO by expanding your content library to address more user queries with relevant information.
How to Optimize For Search Queries?

Optimizing your website to match user search queries is like knowing how to talk to your target audience. It goes beyond just putting keywords in your content. You need to understand what users really want and need.
Remember, search engines try to connect users with the best and most useful information.
Matching Content to User Intent
Start by analyzing the needs of searchers for each query. People who type informational queries typically want helpful explanations, guides, or tutorials. On the other hand, transactional queries indicate readiness to purchase or subscribe.
Therefore, your web page content should reflect these different types:
- Informational searches: Provide how-to tutorials, detailed explanations, or educational posts.
- Transactional search: Present product listings, straightforward pricing, and a clear call to action.
- Navigational queries: Help people reach a particular website or page quickly.
- Branded queries: Ensure official pages rank first so that people find your site or your brand swiftly.
Using Keywords Effectively in SEO
Integrate relevant queries and keywords into your title tags, headings, meta descriptions, and throughout your copy.
However, avoid spammy repetition. The aim is to create a natural flow that addresses user queries while letting search engines parse your content accurately. This increases your chance of showing up for both short-tail and long-tail searches.
Be mindful of local references if you have a location-based offering, and remember that sometimes users might specify something like “SaaS link building agency Los Angeles,” so mention local details if it applies.
Another point is to keep best practices in mind. Write your content for humans first, ensuring clarity and depth, then weave in your relevant keywords to help search engines connect you with the correct search queries. Because user queries shift over time, your strategy should adapt. Refreshing older content or adding new posts ensures you stay current with search query trends.
Are There Tools to Help Categorize Different Types of Search Queries?

Yes. Many SEO platforms and analytics tools can segment queries by search intent.
Some solutions might label them as informational queries, navigational queries, or transactional search queries automatically. Others allow custom tags so you can mark queries that appear to be brand-focused or interest-focused.
Here are a few commonly used resources:
- Google Search Console: Offers insight into queries that lead to clicks on your site.
- Third-Party SEO Software: SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Moz can reveal queries, show search volumes, and indicate competition levels.
- Search Engine Keyword Planner: For instance, Google Ads Keyword Planner can reveal potential traffic from specific search terms.
Using these tools consistently lets you see the search query type, refine your approach, and check if the results match your goals.
Search Query Examples
Below are some simplified search query examples and how they might categorize:
- “VH Info Homepage”: Navigational search query, as the user is looking for a particular website.
- “why SaaS link building is important”: Informational search query, showing the user wants more knowledge on a topic.
- “buy CRM software for sales teams”: Transactional search query, indicating readiness to purchase.
- “testimonials for VH Info link building”: Branded query, referencing a specific brand name plus a specific request.
- “list of top SEO blogs in Los Angeles”: Informational searches, with a slight local angle. Could also be partially navigational if they are thinking of a certain site but cannot recall it.
- “how to manage ppc ads for SaaS”: Informational queries, focusing on best practices or processes around paid advertising.
Each example highlights how user queries often contain clues about search intent. Paying attention to findings like these is an essential part of refining your approach.
FAQ’s:
How Do Search Queries Impact SEO?
Search queries reveal the language people use and what they hope to find. By matching your content and metadata to user queries, you boost your ranking potential in organic search.
Also, search queries show you where to expand your content, such as creating new category pages or blog posts addressing popular questions. These strategies help you deliver relevant results to your target audience.
Can I Optimize My Site For All Types of Search Queries?
It is possible to structure your site so each query type receives an appropriate response.
- For navigational search queries, ensure your brand site appears at the top.
- For informational queries, create high-value guides or articles.
- For transactional queries, develop user-friendly product listings or landing pages.
Although you can cover various types of queries, focus on the ones that align with your goals and your specific industry niche.
How to Find Search Queries That Will Generate Sales?
Review your Google Search Console data, check your current keywords, and cross-reference them with business metrics like conversions or signups. Identify queries that include words like “purchase,” “order,” “buy,” or “subscription.”
These are strong indicators of transactional search. In addition, you can use Google Ads data or PPC Ads metrics to see which queries lead to immediate actions. Once found, optimize your pages to capture those searchers more effectively.
Which Types of Queries Help You Improve the Findability?
Informational searches can boost your visibility when you provide high-quality resources that people share. Transactional queries can help you show up for individuals ready to make a purchase. Navigational queries can secure your brand name position in search results.
Overall, combining all these types helps you improve findability across an array of user needs.
How Can I Identify the Search Intent Behind a Query?
Look for contextual clues in the search term. Words like “buy,” “subscribe,” or “order” hint at transactional search. Phrases like “how to” or “what is” generally belong to informational search queries.
Queries with a brand name or product name plus some navigational terms can signal navigational queries. If the query is specifically referencing your brand or a competitor brand, that is typically a branded query.
Some tools automate this analysis, labeling user queries automatically so you can see the likely intent.
Conclusion
Search queries are crucial for search marketing success. They reveal user intent, guiding content optimization and product offerings.
Understanding different query types and using strategic keywords can help boost conversions and brand awareness.
Modern tools simplify query categorization and site optimization, ensuring a steady flow of traffic and revenue. Success lies in aligning with user intent, providing valuable answers, and adapting to new data for sustainable growth in search rankings.



