Duplicate content is one of the most common technical SEO issues that can have a significant negative impact on a website’s search engine rankings and organic traffic.
As an SEO expert or website owner, it’s important for you to understand what duplicate content is, why it matters for SEO, and how to find and fix any duplicate content problems on your site.
In this comprehensive guide, the team at VH Info breaks down everything you need to know about duplicate content and SEO.
We’ll cover what counts as duplicate content, why it’s bad for SEO, common causes, how to identify duplication, and most importantly – proven strategies to resolve any duplicate content issues to improve your rankings and traffic.
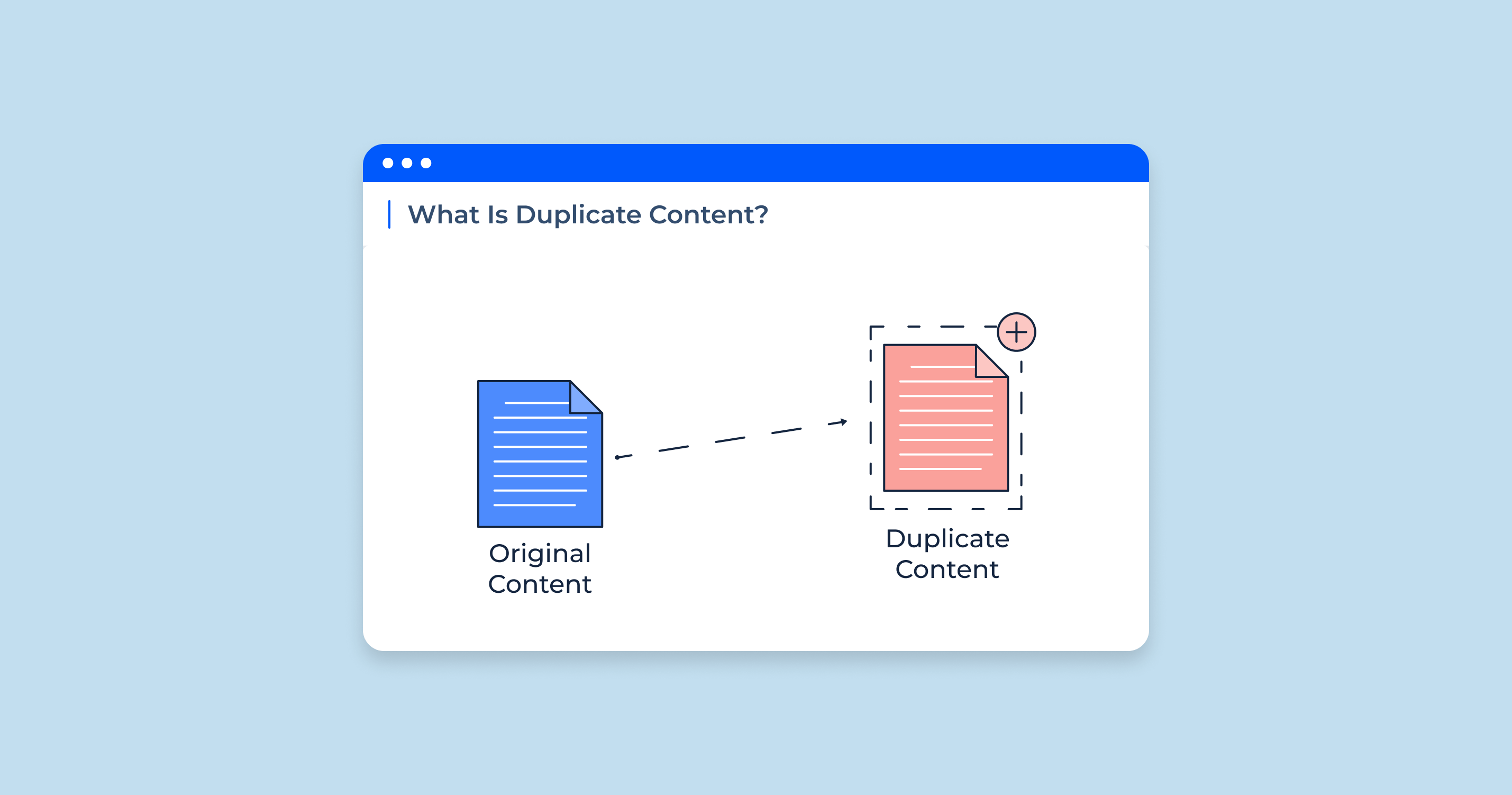
What is Duplicate Content in SEO?

In the context of search engine optimization (SEO), duplicate content refers to substantive blocks of content within or across domains that either completely match other content or are appreciably similar. Duplicate content can occur on multiple pages within your website or across different websites.
Duplicate content is not limited to just blog posts or articles. It can also include product descriptions, meta descriptions, and any other text-based content on web pages. Even slight variations of the same content on different pages or sites can get flagged as duplicate content by search engine crawlers.
Why Does Duplicate Content Matter?
Duplicate content can negatively impact SEO in several key ways:
For Search Engines
When search engines like Google encounter duplicate content, it presents three main challenges:
- They don’t know which version(s) to include/exclude from their indices.
- They don’t know whether to direct the link equity (authority, anchor text, etc.) to one page, or keep it separated between multiple versions.
- They don’t know which version(s) to rank for relevant search queries.
As a result, search engines may not properly index pages with duplicate content or may rank the wrong version. This leads to lower visibility in search results.
For Site Owners
For website owners, duplicate content often leads to:
- Diluted visibility in search results, as search engines rarely show multiple versions of the same content. This forces them to choose a canonical version, diluting the visibility of each duplicate.
- Diluted link equity, as inbound links get split between the duplicates instead of pointing to one authoritative version. Since links are a key ranking factor, this dilution can significantly impact search rankings.
The net result is that the content doesn’t achieve the search visibility it otherwise would if the duplicate issue didn’t exist. Website owners may suffer lower rankings and reduced organic traffic.
Why is Having Duplicate Content an Issue For SEO?

There are several reasons why having duplicate content is problematic for SEO:
- It can dilute your ranking potential. When the same content appears on multiple URLs, it’s difficult for search engines to determine which version is most relevant to rank. As a result, they may not rank any of the versions as high as they would if there was a single authoritative version.
- It wastes crawl budget. Search engine crawlers have a limited crawl budget for each site. Duplicate content results in crawlers wasting time indexing the same content multiple times, taking away from the crawl budget for your unique content.
- It can cause indexing issues. In some cases, search engines may identify the duplicates and choose to index only one version, filtering the others out of search results entirely. If the version they choose isn’t the one you want to rank, it can really hurt your SEO.
- It makes it harder to attract links. When multiple versions of a piece of content exist, any inbound links get split between them, diluting the link equity and authority of each version. Consolidating duplicate content helps attract more links to a single authoritative URL.
- It provides a poor user experience. Duplicate content also negatively impacts users, leading to frustration when they encounter the same content multiple times. This can increase bounce rates and reduce time on site.
5 Common Causes Behind Accidental Duplicate Content
Most duplicate content is not created intentionally. Here are some of the most common technical causes of duplicate content:
1. Improperly Managing WWW and Non-WWW Variations
If your site is accessible with both “www” and “non-www” versions of URLs (http://example.com and http://www.example.com), search engines will see these as two separate sites with duplicate content. It’s important to choose one version and redirect the other to it.
2. Granting Access With Both HTTP and HTTPS
Similarly, if your site allows access through both HTTP and HTTPS protocols, it can create duplicate versions of each page. Always redirect HTTP to HTTPS, especially if you’ve already implemented SSL.
3. Using Both Trailing Slashes and Non-Trailing Slashes
Having URLs accessible with and without a trailing slash (like /page/ and /page) creates duplicate content. Choose one convention and stick with it.
4. Including Scraped or Copied Content
Scraped or copied content, even if it’s unintentional, counts as duplicate content. Be sure to always create original content.
5. Having Separate Mobile and Desktop Versions
Separate mobile and desktop versions of your site on different URLs (like m.example.com) can create duplication. Use responsive design instead.
Types Of Duplicate Content in SEO
Duplicate content can be categorized into a few main types:
1. Internal Duplicate Content:
When the same content appears on multiple pages within a single website.
2. External Duplicate Content:
When the same content appears across different websites.
3. Near-Duplicate Content:
Content that is very similar but not identical, often due to minor edits or changes.
4. Cross-Domain Duplicate Content:
Identical content that appears on different domains or subdomains owned by the same company.
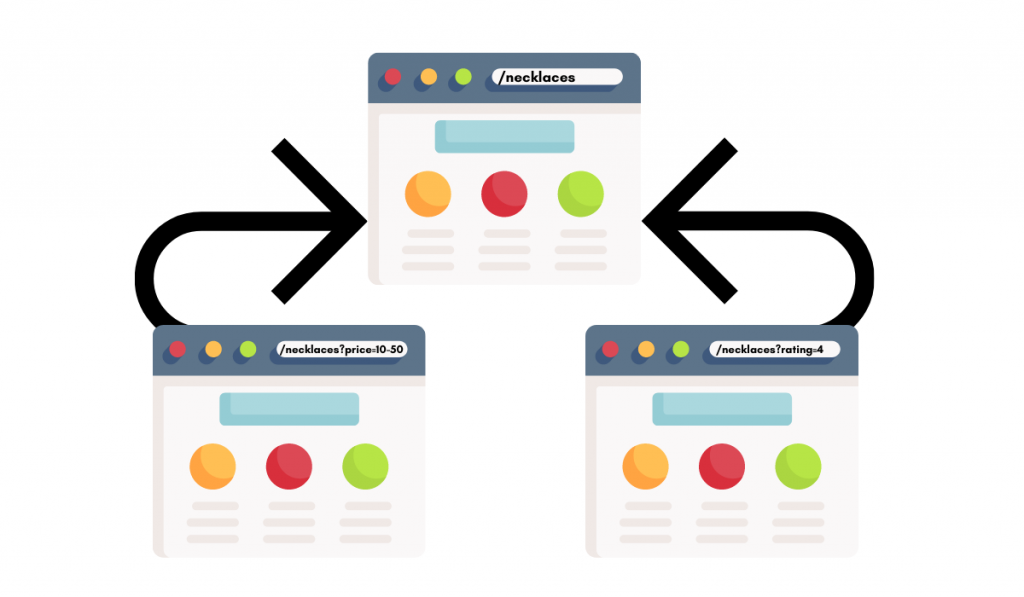
5. Duplicate Content From URL Variations:
Duplicate pages created by appending certain parameters to URLs, like click tracking or session IDs.
6. Scraped Content:
Content copied or “scraped” from other sources without adding any original value.
7. Boilerplate Content:
Reused generic content like product descriptions or company information across multiple pages.
8. Syndicated Content:
Content republished on other sites through syndication, like articles or press releases.
What Does Duplicate Without User-Select Canonical Mean?
“Duplicate without user-selected canonical” is a status in Google Search Console indicating that Google found duplicate content on your site but did not index it because you didn’t specify a canonical URL.
This happens when Google finds multiple identical or very similar pages on your site, but none of the pages have a canonical tag telling Google which version you want to be indexed. Without this signal, Google doesn’t know which URL to show in search results, so it may choose not to index any of the duplicates.
Does Google Penalize Duplicate Content?
Google does not have a direct penalty for duplicate content, unless it appears to be a deliberate attempt to manipulate rankings or deceive users. However, even without a penalty, duplicate content can still hurt your SEO if search engines don’t index your preferred version or split link equity between the duplicates.
While you likely won’t face a manual penalty for duplicate content, it’s still important to fix it to avoid the other negative SEO impacts. Duplicate content can hold your site back from reaching its full potential in search. Using a plagiarism checker can help you identify duplicate content and make necessary adjustments before publishing.
Finding Duplicate Content
There are two main areas where you’ll want to look for duplicate content – within your own website and externally across other sites.
Finding Duplicate Content Within Your Own Website
To find duplicate content on your own site, you can:
- Run a crawl of your site with a tool like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to identify duplicate page titles, descriptions, and body content.
- Use Google Search Console to check for duplicate title tags, meta descriptions, and H1s under the “HTML Improvements” report.
- Do a site: search in Google for a unique snippet of content in quotes to see if it appears on multiple pages.
- Use a duplicate content checker tool like Siteliner to scan your site for internal duplication.
Finding Duplicate Content Outside Your Own Website
To check for external sites duplicating your content, you can:
- Do a Google search for a unique quoted snippet of your content to see if it appears on other domains.
- Set up Google Alerts for unique phrases to get notified of copies appearing on other sites.
- Use a plagiarism checker tool like Copyscape to scan the web for copies of your content.
- Check referral traffic in Google Analytics for suspicious sites that may have scraped your content.
How Do You Fix Duplicate Content?

The best method to resolve duplicate content depends on the specific situation, but here are some of the most common fixes:
- Use 301 redirects to consolidate duplicate pages into a single canonical URL. This tells search engines which version to index while still sending any link authority to that page.
- Implement canonical tags to specify the preferred version when you have multiple pages with similar content that you want to keep live (like product variants).
- Use the parameter handling tool in Google Search Console to tell Google how to handle URLs with specific parameters, like filtering out session IDs.
- Block search engines from indexing duplicate content using robots.txt or meta robots tags when you don’t want those pages showing up in search at all.
- Rewrite and improve thin or duplicate content to make it unique and valuable. This is especially important for boilerplate or templated content.
- Reach out to webmasters to remove content scraped from your site. You can also file a DMCA takedown request in cases of blatant theft.
- Use responsive design rather than separate mobile URLs to avoid cross-device duplication.
Best Practices to Avoid Duplicate Content
In addition to fixing existing duplicate content issues, it’s important to put best practices in place to avoid new duplication in the future:
- Always use canonical tags, even on unique pages, to clearly indicate the authoritative version.
- Implement 301 redirects whenever you change or remove a URL to avoid leaving duplicate versions behind.
- Set a preferred domain (www vs. non-www) in Google Search Console.
- Avoid boilerplate content whenever possible and write unique copy for each page.
- Minimize the use of URL parameters and use the URL Parameter Handling tool in Google Search Console.
- Regularly audit your site with crawling tools to catch any new duplicate content issues.
- When syndicating or reposting content, always use canonical tags pointing back to the original version.
What Does Google Consider Duplicate Content?

Google considers content to be duplicate when it is “appreciably similar” to content elsewhere on the same site or on another site.
Here are some common examples:
Identical Web Pages
Pages that contain the exact same content, either within the same site or across domains. This is the clearest example of duplicate content.
Template Content
Boilerplate content that is reused across multiple pages with little to no unique content on each page. Common on ecommerce sites with product descriptions.
Bad Rewrites Of Existing Pages
Attempts at rewriting content that end up being too similar to the original, often in an effort to target multiple keywords. These are seen as duplicate by Google.
Blog Articles Posted Twice
Reposting blog content in full on your own site (like moving from a subdomain), on other sites you own, or on external sites without using canonical tags.
FAQ’s:
Are Duplicate Images Bad For SEO?
While Google is primarily concerned with duplicate text content, having the same image appear multiple times across your site (like a logo or banner) isn’t ideal for SEO. It can slow down page load times and eat up crawl budget. Use canonical tags for images when possible.
Does Deleting Duplicate Pages Hurt Your SEO Results?
Deleting duplicate pages and properly redirecting them to the canonical version with a 301 redirect generally has a positive impact on SEO. It consolidates link equity and avoids keyword cannibalization. Just be sure to redirect any deleted pages to avoid 404 errors.
Is Duplicate Content On Different Domains Problematic?
Yes, duplicate content across different domains is a problem. Google indexes each unique domain separately, so cross-domain duplication can result in the same negative SEO impacts as internal duplication. Use canonical tags to specify the original source for content reposted on other domains.
How Are Canonical Tags Utilized to Fix Duplicate Content Issues?
Canonical tags (rel=”canonical”) are used to tell search engines which version of a duplicated piece of content is the “canonical” or preferred version. This consolidates ranking signals like link equity to that version, even when the content remains accessible on multiple URLs.
Can Google Search Console Provide Insights into Duplicate Content Issues?
Yes, Google Search Console offers a few reports that can surface duplicate content on your site, including:
- The “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” status in the Index Coverage report shows duplicate content that doesn’t have a canonical tag.
- The “Duplicate title tags” and “Duplicate meta descriptions” reports under “HTML Improvements” flag duplicate titles and descriptions site-wide.
Can I Get a Penalty For Having Duplicate Content?
Google has confirmed that there is no duplicate content penalty. However, it can still impact your search visibility if Google doesn’t choose the version you want to rank or splits link equity between the duplicates.
How Do You Check For Duplicate Content?
You can check for duplicate content by running a site crawl with a tool like Screaming Frog, using Google Search Console reports, doing site: searches in Google, or using duplicate content checker tools.
How Much Duplicate Content is Acceptable?
While there is no defined threshold, it’s best to keep duplicate content to a minimum. Even 20-30% duplicate content can start to impact SEO. Focus on creating unique, valuable content.
Is Duplicate Content Still Bad For SEO?
Yes, duplicate content is still bad for SEO. While Google has gotten better at handling it, duplication can still hurt your rankings and organic traffic if not properly addressed.
Is Duplicate Content illegal?
Duplicate content itself is not illegal, but copying content from other sites without permission could be considered copyright infringement in some cases.
Conclusion
Duplicate content is a common technical SEO issue that can have significant consequences for your organic search performance. It can dilute your ranking potential, waste crawl budget, cause indexing issues, and provide a poor user experience.
Understanding what is duplicate content, how to spot it, and the steps to resolve it can help. Managing duplicates correctly improves your site’s optimization and maximizes its search potential.
At VH Info, we specialize in providing actionable insights and strategies to improve your SEO and link building efforts. Our team of experts can help you identify and resolve duplicate content issues to boost your rankings and traffic.



