Introduction
Product management has taken center stage in several businesses in today’s digital age. Understanding the subtleties of this industry is critical, whether it be digital product management or retail product management. Dive into this detailed handbook to learn the secrets of effective product management.
What is Product Management ?
 Product management entails the planning, forecasting, and marketing of a product across its entire lifespan. It entails the coordination of many teams, from design to marketing, to ensure the product’s commercial success. Unlike other positions, “product management Monday” rituals include an in-depth examination of market trends and customer input in order to continuously enhance product strategy.
Product management entails the planning, forecasting, and marketing of a product across its entire lifespan. It entails the coordination of many teams, from design to marketing, to ensure the product’s commercial success. Unlike other positions, “product management Monday” rituals include an in-depth examination of market trends and customer input in order to continuously enhance product strategy.
Difference between Product Management & Project Manager
 While both professions include coordination and planning, product management focuses on directing a product’s path based on market demands. A project manager, on the other hand, concentrates on execution, ensuring that tasks are done on schedule. The emphasis in product management marketing is on understanding client wants, whereas a project manager focuses on resource allocation and timelines.
While both professions include coordination and planning, product management focuses on directing a product’s path based on market demands. A project manager, on the other hand, concentrates on execution, ensuring that tasks are done on schedule. The emphasis in product management marketing is on understanding client wants, whereas a project manager focuses on resource allocation and timelines.
Strategic Function of Product Management
Product management is an important strategic role. Product managers are tasked with defining a product’s general purpose for existence, the product’s why ?
They are also in charge of conveying product goals and strategies to the rest of the firm. They must make certain that everyone is working towards a common organizational aim.
Product management entails a wide range of continuous strategic duties. They should not be in charge of the low-level aspects of the development process.
Innovative organizations segregate this job and delegate tactical parts like scheduling and task management to project managers. This discrete separation frees up the product manager to concentrate on the higher-level strategy.
5 Steps of Product Strategy
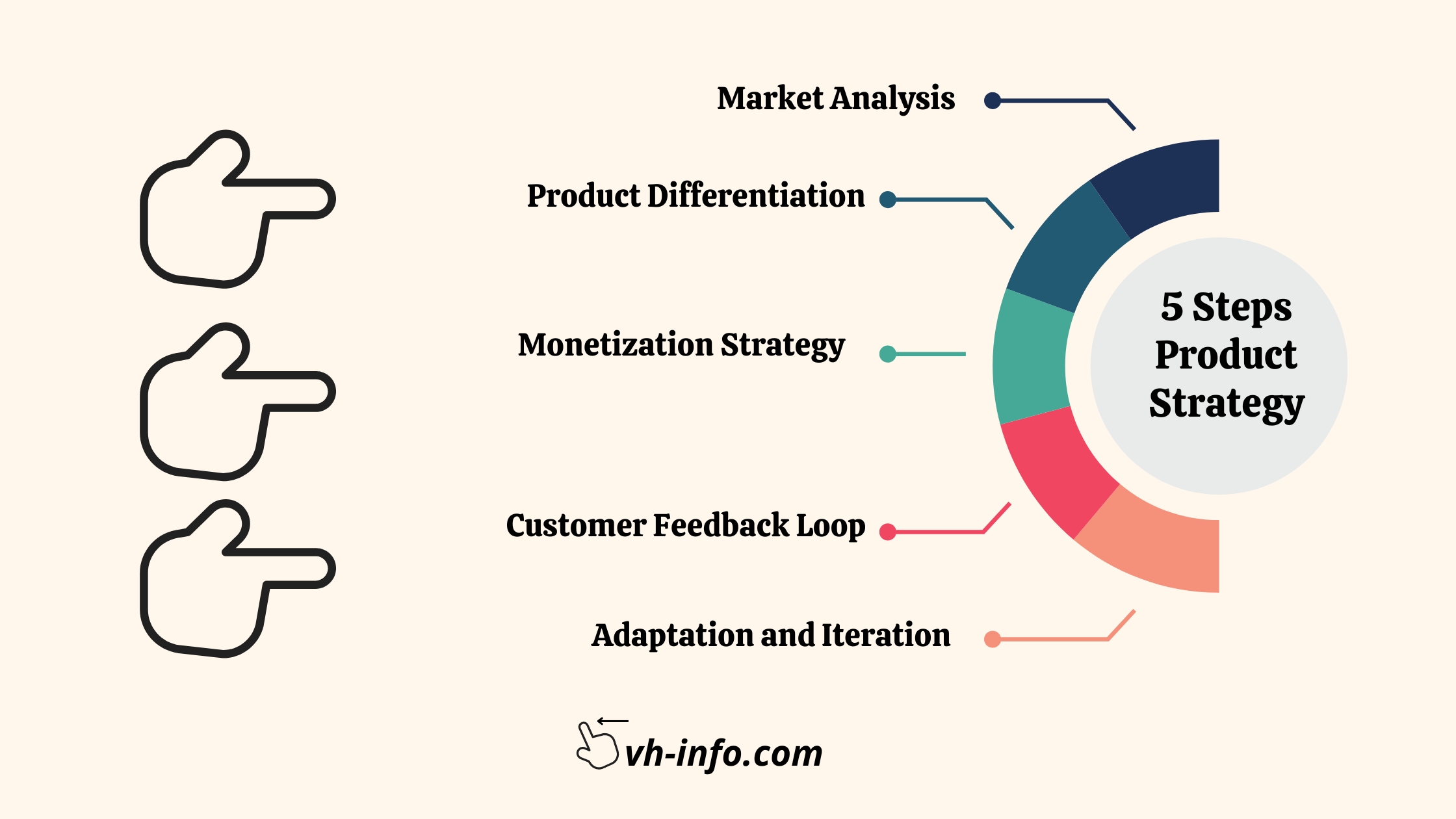 Market Analysis:
Market Analysis:
Market research is the first stage in developing a product strategy. It entails extensive study and comprehension of the market in which the product will compete. Identifying the target audience’s needs, preferences, and pain areas is part of this process. It is critical to analyze market trends, competitors, and possible opportunities. The idea is to learn about the present environment and find holes that your solution may address.
Read More:What Will Digital Marketing Look Like In 2023? A Look At The Tools And Software Trends
Product Differentiation:
Product differentiation refers to the distinct qualities and characteristics that distinguish your product from competitors in the market. This phase is articulating the value proposition of your product – what makes it unique and why buyers should select it over alternatives. Innovative features, improved quality, a better user experience, a price strategy, or a mix of these elements can all contribute to product distinctiveness. The idea is to provide them a strong and compelling reason to buy your goods.Monetization Strategy :
The monetization strategy describes how you intend to make money from your product. Pricing methods such as subscription-based, one-time purchase, freemium, or tiered pricing must be chosen. Your monetization plan should be in line with your target market’s willingness to pay, the perceived worth of your product, and the industry’s broader price structure. It is critical to establish a balance between revenue maximization and customer value.
Read More:The Power of Personalization: Customizing Your Content Strategy for Your Target Audience
Customer Feedback Loop :
Consumer input is essential for product enhancement and consumer pleasure. Creating a feedback loop entails putting in place tools to collect and analyze user feedback. This might involve surveys, user testing, encounters with customer service, and monitoring internet reviews. Actively listening to your consumers allows you to find pain spots, places for improvement, and potential new features that might increase the value of your product.Adaptation and Iteration :
The market is ever-changing, and client tastes shift over time. Adaptation and iteration imply a dedication to improving your product in response to customer input and changing market conditions. This level necessitates responsiveness to client requests, problem resolution, and continual product enhancement. Regular updates, new additions, and enhancements based on real-world usage contribute to your product’s durability and relevancy.
Read More:Maximising Conversions: Effective Bottom-of-the-Funnel Strategies
What is the Product Management Process ?
 The Product Management Process is a set of actions that product managers and teams must take to ensure a product’s successful development, launch, and growth. Although the process varies from organization to organization and even from product to product, there are generally agreed steps that most businesses follow. Here is a breakdown of the typical stages:Idea Generation/Discovery: This is the beginning place for developing new product concepts. Customer input, market research, internal brainstorming sessions, or observations of market trends and gaps can all lead to it.Market Research and Validation: It is critical to validate a concept after it has been produced. This entails investigating the target market, comprehending client wants, evaluating competitors, and determining the potential magnitude of the opportunity. The purpose is to ensure that there is true demand for the product and that it is buildable.
The Product Management Process is a set of actions that product managers and teams must take to ensure a product’s successful development, launch, and growth. Although the process varies from organization to organization and even from product to product, there are generally agreed steps that most businesses follow. Here is a breakdown of the typical stages:Idea Generation/Discovery: This is the beginning place for developing new product concepts. Customer input, market research, internal brainstorming sessions, or observations of market trends and gaps can all lead to it.Market Research and Validation: It is critical to validate a concept after it has been produced. This entails investigating the target market, comprehending client wants, evaluating competitors, and determining the potential magnitude of the opportunity. The purpose is to ensure that there is true demand for the product and that it is buildable.
Read More: Marketing ResearchProduct Definition and Planning: With a verified product idea, you may go on to establishing the product’s specifications. This might include writing user stories, establishing objectives and key outcomes (OKRs), and developing a product roadmap. It is about developing a clear vision and strategy for the product.
Read More: Product Planning Design and Development: This is the stage at which the finished work begins to take shape. Mockups and prototypes are created by designers, while coding begins by developers. Collaboration between design, development, and product management is critical to ensuring that the product satisfies the demands of users while also meeting corporate objectives.
Read More:Top Benefits of Developing Testing: The product is rigorously tested before it is issued. This includes unit testing, user acceptance testing (UAT), beta testing, and other types of testing. The purpose is to find and resolve issues, confirm that the product fits specifications, and assess usability.Launch: After testing is completed, the product is released to the market. Depending on the product and market strategy, this might entail a phased or regional launch. Close monitoring is required to resolve any unanticipated concerns as soon as possible.Feedback and Iteration: Following the product’s introduction, users submit frequent feedback to help understand how it works, what works, and what doesn’t. This feedback is used to direct future revisions and improvements.Growth and Scaling: As the product gains traction, steps to expand the user base and income are implemented. Marketing activities, partnerships, product updates, and other projects may be included.Product Maintenance: Products require updates, fixes, and sometimes even overhauls over time. Maintaining a product entails guaranteeing its continuing functionality, security, and market relevance.Retirement/End-of-life: Not all items are indestructible. Some items may need to be decommissioned or replaced depending on market trends. This step entails gracefully retiring a product, maybe by incorporating its features into another offering or ensuring a seamless transition for current consumers.
6 Skills of Product Management
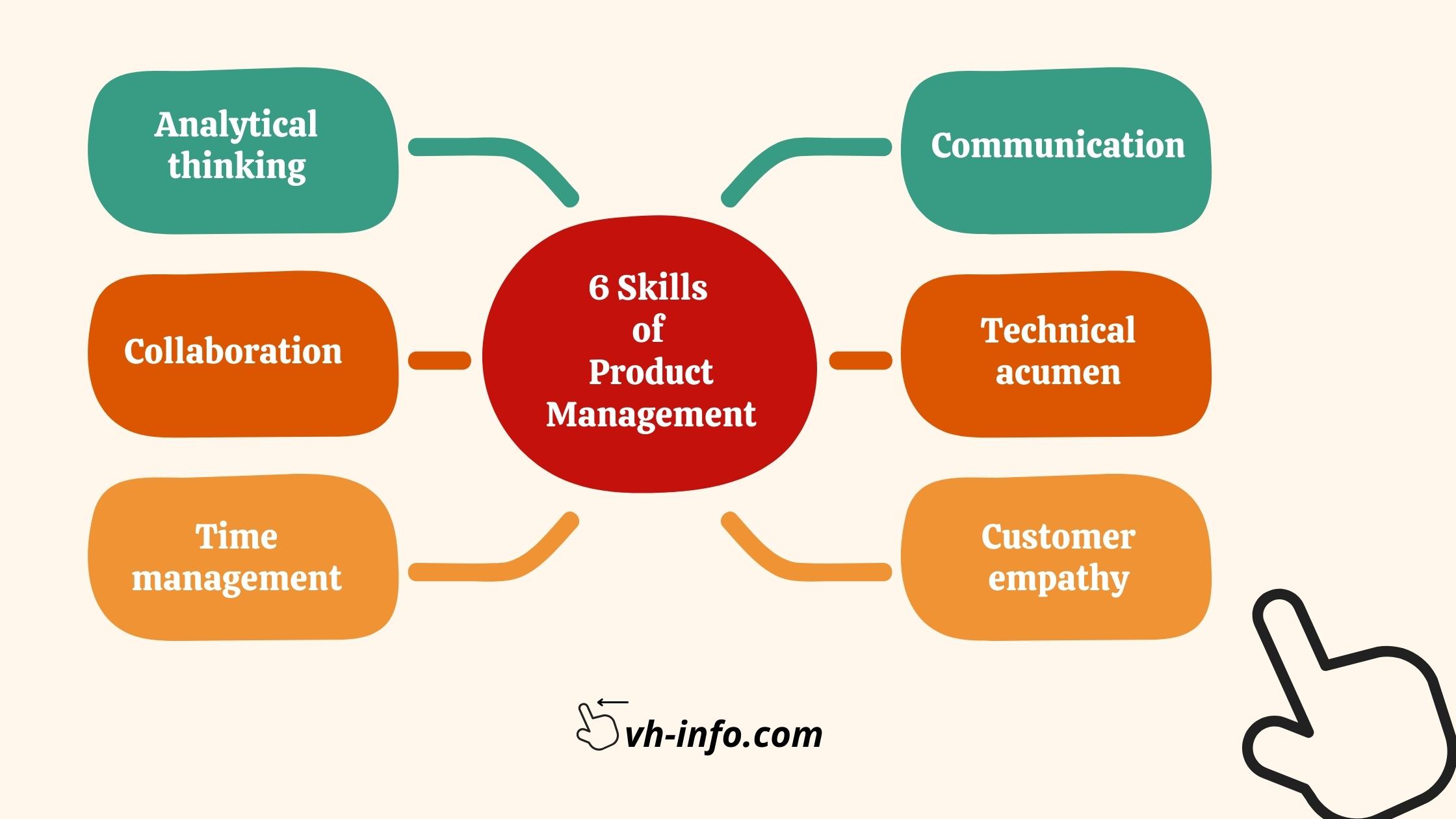 Analytical thinking :
Analytical thinking :
To make educated judgments, product managers must be skilled at analyzing data, market trends, and consumer feedback. They must be able to understand complicated data, find trends, and make conclusions in order to steer product development initiatives. They may prioritize features, manage resources, and ensure that product decisions correspond with corporate goals by using analytical thinking.Collaboration :
Product managers work with multi-functional teams that include engineers, designers, marketers, and salespeople. Collaborative abilities are essential for creating a coherent working environment in which team members from disparate disciplines can focus their efforts towards a common product goal. Effective cooperation ensures that all points of view are taken into account, resulting in superior product outputs.Time management :
Time management is critical in the fast-paced world of product development. Product managers are in charge of fulfilling deadlines, managing tasks, and keeping the product development process on track. Effective time management enables them to balance conflicting goals and deliver things on time.Communication :
Product management success is built on clear and straightforward communication. Product managers must communicate their ideas, product vision, and requirements to various stakeholders such as team members, executives, customers, and users. Strong communication skills promote alignment, reduce misunderstandings, and enhance team cooperation.Technical acumen :
While product managers may not need to be highly technical, they must have a basic grasp of technology and the development process. This expertise enables them to have meaningful conversations with engineers, make educated technical decisions, and bridge the technical and non-technical team members’ divide.Customer empathy :
Understanding and empathizing with clients is critical for developing goods that actually match their requirements. Product managers must be able to put themselves in the shoes of their customers, collect feedback, and push for products and enhancements that will improve the user experience. This ability guarantees that the product remains focused on the client.
5 Steps to connect to your Product Road Map
 Review and Iterate :
Review and Iterate :
Review the progress of your product plan on a regular basis and make changes as needed. This includes determining if milestones are being fulfilled, tracking feature development, and revising priorities in response to changing market conditions, user input, or other unanticipated events. Iteration is essential for keeping the roadmap current and adaptable to changing conditions.Align with Stakeholders :
Alignment of stakeholders is critical for the success of your product strategy. Engage key stakeholders like executives, product teams, marketing, sales, and customer service to ensure that everyone is on the same page about the product’s goals, features, and timescales. Regular communication and collaboration develop a common understanding and allow for modifications in response to feedback and shifting priorities.Set Milestones :
Milestones are noteworthy successes or phases in the product development schedule. Divide the product plan into smaller, more manageable portions with clear milestones. These may be associated with feature releases, testing phases, user feedback cycles, or other significant events. Milestones offer a disciplined method for tracking progress, ensuring responsibility, and measuring the effectiveness of the product development process.List Features and Priorities :
Identify and list all of the product’s features and functions. It is critical at this point to incorporate cross-functional teams in order to acquire varied opinions. Once you’ve compiled a detailed list, prioritize the features based on customer wants, market trends, potential effect, and technical feasibility. Prioritization guarantees that the most important and useful features are created first.Define Vision :
The product vision establishes the product’s ultimate objective and purpose. It explains the long-term future of the product and offers a clear direction for the team. Defining a compelling vision aids in the alignment of all stakeholders, from development teams to executives, around a single goal. The vision acts as a guidepost, directing decisions and ensuring that each feature and milestone contributes to the overall strategic aim.
Monday.com Product Management Operations
Monday.com offers a comprehensive platform for product management operations. Its organized process may help digital product management teams, while its inventory and sales monitoring tools can help retail product management. Product management internships frequently emphasize understanding technologies such as Monday.com, owing to their industrial significance.
Conclusion
Product management is an ever-changing field that necessitates a diverse set of talents, techniques, and technologies. Understanding the fundamental principles and techniques is critical whether you’re heading into digital product management or attempting to master product management marketing. Remember that in product management, every Monday is a chance to redefine and enhance your product’s trajectory.Q1 : How can product management leverage market rhythms ?
Taking advantage of market rhythms is critical for good product management. The regular patterns, trends, and cycles that sectors and markets go through are referred to as market rhythms.Q2. What is Product Content Management ?
Product material Management (PCM) is the process of developing, organizing, managing, and distributing product material throughout its lifespan. This information includes product descriptions, photos, specs, price, marketing brochures, user manuals, and any other related documents.Q3. What is Product Line Management ?
Product Line Management entails the strategic planning, development, and management of a collection of linked goods aimed at a given market sector or consumer demand. A product line is a collection of items that have comparable qualities, features, and branding and are frequently positioned together to meet certain client needs.
Raj Panchotiya
Raj Panchotiya is a Head of link-building projects at vh-info. He loves to talk about Marketing and Social media. In his free time, he likes to read & stay updated on the marketing!
You can always reach out to Raj on LinkedIn.



